Table of Contents
A snapshot captures the state of a disk at a specific point in time, often relying on the original data and using less space. Whereas, a disk image is a full copy of a disk’s contents and structure, typically used for backups or cloning.
Backing up data is crucial for enterprises to ensure speedy recovery in the event of disaster or system failures. Gone are the days of bulky physical media for backups which require tons of other controls such as safety, transport, media checks for errors, their routine maintenance etc. as enterprises moving to cloud based computing environments the new technologies emerged to support redundancy, faster recovery from such scenarios. Snapshots and disk images are new ear methods to secure digital assets.
In today’s article we understand and compare types of mechanisms to support faster recovery and redundancy – Snapshot and disk images, features of both, differentiate between the two techniques and use cases.
What is Snapshot
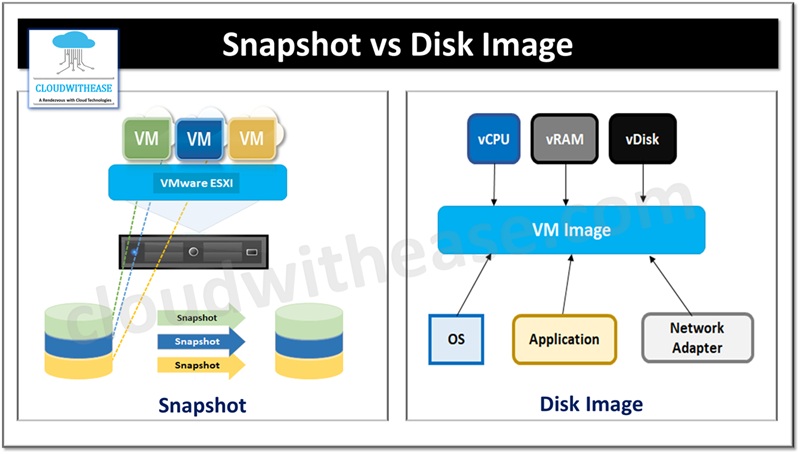
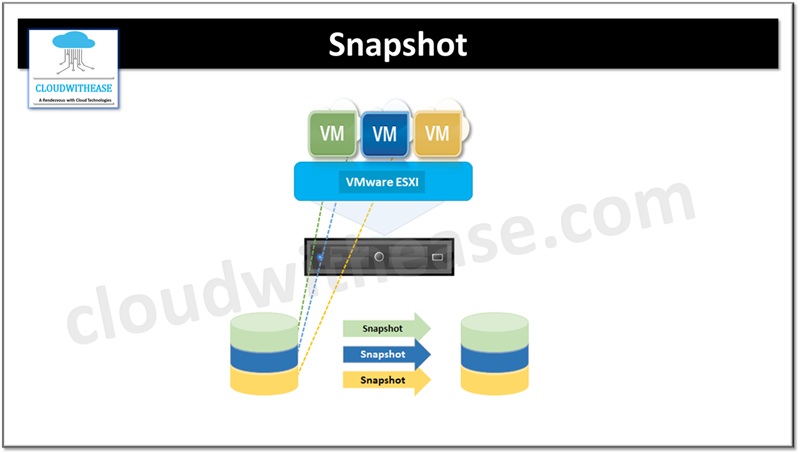
Snapshot is used to record the virtual state of a virtual machine (VM) and data for point in time. It is similar to a standard operating system snapshot on a physical machine. For specific scenarios such as migration, creation of multiple instances of the same VM.
- A VM snapshot is created which is a clone of an existing VM.
- It can also be used to restore a VM to a state it was in before making changes in its configuration.
- Files and extensions created by snapshot are stored on the same storage as the host system.
- Snapshot files have. vmdk extension which is a virtual disk having raw data in the base disk.
- .vmsn file stores the current state of VM and its configuration.
- Delta.vmdk file is an incremental disk capturing all changes between last snapshot and current state of virtual disk.
- Vmsd file has snapshot metadata and information.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Snapshots
Pros
- Faster and speedy rollback to previous state compared to backups
- Quick and easy recovery without any impact on production
- Eliminate need for native backup solutions and reduction in TCO
- Not required to be maintained once purpose is served hence storage cost is saved
Cons
- Prone to disruptions which can impact production system
- Primary storage capacity is largely consumed
- Can’t restore individual files in snapshot
Use Cases for Snapshot
- Used for version control or mitigate any potential damage to a system before its upgrade, migration, or updating OS version, uninstallation of some components etc
- Point in time recovery scenarios for protection against hardware failures or data corruption
What is Disk Image
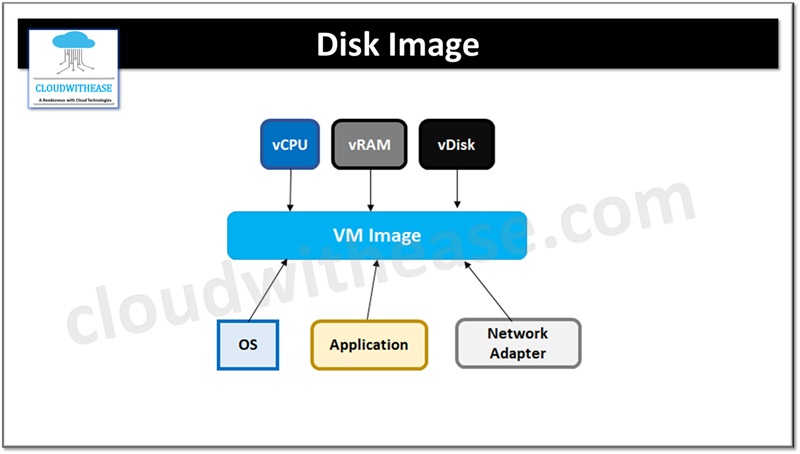
Disk image is an executable file from a virtual machine which has its own unique format. Using the disk image a new VM can be built. It allows for separation of different configuration settings. Ease of deployment and decommissioning is a key feature of disk images. Using a disk image, the complete environment including OS, database and application can be moved to another server.
Advantages and disadvantages of Disk Image
Pros
- Disk images are compressed and stored on a secondary storage device or cloud storage
- Support granular data restoration such as individual files
- Can be created for running disks
- Easy and faster to create
Cons
- Disk images can’t be created during running instances
Use cases for Disk Images
- Boot disk creation
Snapshot vs Disk Image
Below table summarizes the difference between the two:
| Features | Snapshot | Disk Image |
|---|---|---|
| Creation | Created while disks are running even while attached to instances which are running | Can’t be created while instances are running |
| Ease of use | Creation is easier and can upload without VM is stopped | Meant for re-using compute engine states while creating new instances |
| Usage | Ideal for backup and recovery scenarios and meant for regular uploads and infrequent downloads | Ideal for boot disk creation and meant for regular downloads |
| Features | •Speedy to create •Snapshots are usually incremental and not bulky as they do not contain OS •Snapshots have complete VM machine including RAM, CPU state, device state and all writable disk contents | •If same image is downloaded multiple times, then subsequent downloads are faster •Disk images is a full including OS, database, application etc. |
Download the comparison table: snapshot vs disk image