Table of Contents
Today’s businesses are faced with the challenge of improving performance and lowering costs at the same time. It’s challenging because they need to find ways to reduce latency and storage while dealing with limited bandwidth, computing, and storage resources.
Edge computing is an emerging technology that is set to make a big impact on businesses in the coming years. In this blog post, we’ll introduce you to edge computing and explain why it’s so important for businesses today. We’ll also share some details about different types of edge computing and provide examples of how companies are currently using this technology.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is an IT concept that was first proposed in the early 2000s. Simply put, edge computing is a distributed computing architecture. It’s a way of processing and storing data at the “edge” or “perimeter” of a network, as close to the source of data as possible.
Yes, it’s not a new technology, but it’s been seeing a lot of interest from businesses over the last few years. For example, Cisco predicts that 10% of organizations will be using edge computing by 2022. So why is edge computing essential for businesses today? Let’s take a look at a few reasons.
Why is Edge Computing so important?
Businesses are experiencing rising demand for real-time services. Customers expect real-time services and are willing to pay more for them. This is making businesses move to a more real-time-focused business model.
But most businesses today use a centralized model where all data is processed in the core of the data center. This centralized model is great for batch-oriented and compute-intensive tasks. However, it’s not ideal for real-time services because it involves a long journey for data to reach the core of the data center.
The distance can be up to 10,000 miles or 16,000 kilometers. In contrast, the edge is usually 100 to 1,000 miles or 160 to 1,600 kilometers from the source of data. This means that data in an edge-based architecture travel only 1/10th or 1/16th of the distance. This short and direct journey makes edge computing ideal for real-time services.
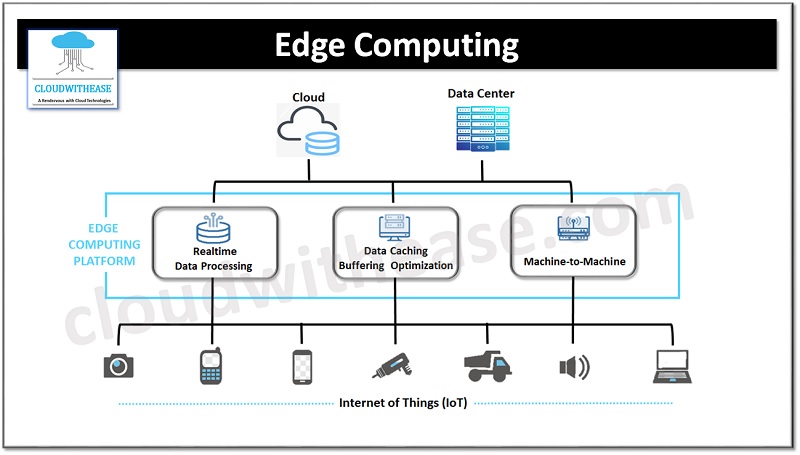
Different Types of Edge Computing
There are many different types of edge computing. We’ll take a look at the most common ones.
- Last Mile Computing – Last mile computing refers to the use of local computing resources as close as possible to the end user. This is a particularly common type of edge computing in telecom companies. For example, telecom companies can use edge computing in their gateways to reduce latency. Gateways are used in the core of the network to connect networks of different providers.
- Fog Computing – Fog computing is another type of edge computing. It lies between last-mile computing and cloud computing. It’s a distributed network of computing resources that are placed at the “edge” of a network, as close as possible to the source of data.
- Cloudlet – Cloudlets are miniature data centers that provide computing services. They are smaller and less expensive than full-scale data centers. Cloudlets are designed for edge computing and provide computing services at the edge of a network. Cloudlets can also provide services for a specific application, which is usually hosted on-premises.
Benefits
Let’s take a look at the top benefits of edge computing.
- Reduced latency – Because data travels shorter distances in edge computing, the latency is reduced. This is beneficial for real-time applications where latency is critical.
- Enhanced security – Because data is not traveling as far, the risk of cyber attacks is reduced. The data is also encrypted during transmission, so it is secure as it travels.
- Improved scalability – Edge computing is ideal for high-growth businesses. It’s easier to scale edge computing as the demand for computing increases. In comparison, cloud computing is more challenging to scale.
- Lower cost – Because edge computing is optimized for specific tasks, it’s cost-effective.
Limitations
While edge computing is beneficial, there are a few limitations that businesses need to keep in mind.
- Limited by bandwidth – The shorter data transmission distance of edge computing comes at a cost. It means that data can’t move at the same speed as data in the cloud. If you use edge computing to save costs, you’ll also have to deal with slower data speeds.
- Requires special infrastructure – You’ll need special hardware for edge computing, such as high-speed network switches. This can be expensive and challenging to manage.
- Can’t host all applications – Because of their reduced capacities, edge computing can’t host all applications. They are most commonly used to host web apps, video streaming services, and IoT applications.
Key takeaway
Edge computing is an emerging technology that is set to make a big impact on businesses in the coming years. In this blog post, we’ve introduced you to edge computing and explained why it’s so important for businesses today. We’ve also covered different types of edge computing and provided examples of how companies are currently using this technology.
