Table of Contents
Storage in cloud computing is very versatile and cloud providers offer a variety of storage types to fulfil different business requirements as per organizations requirements. Blob storage, block storage, file storage, network file storage are some of the types of storage options offered by the majority of cloud providers such as Microsoft Azure, Amazon web services, Oracle cloud, Google cloud services and so on.
Today we look more in detail about storage types namely FSx and EFS offered by AWS, their comparison i.e. Amazon FSx vs EFS understanding the key differences and use cases.
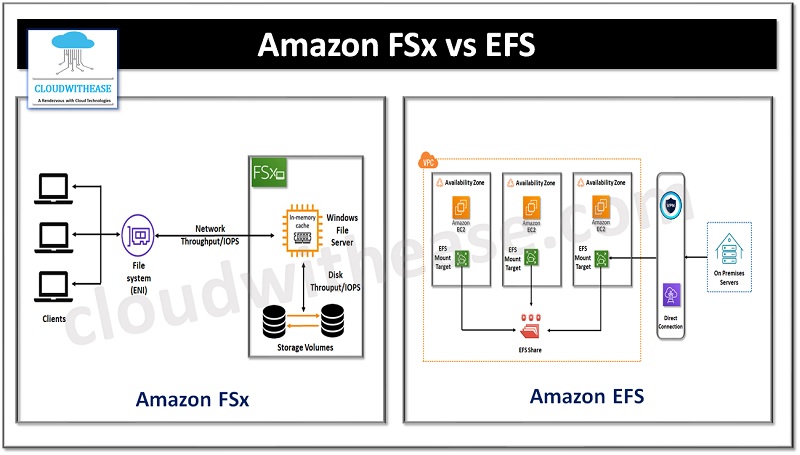
What is Amazon FSx?
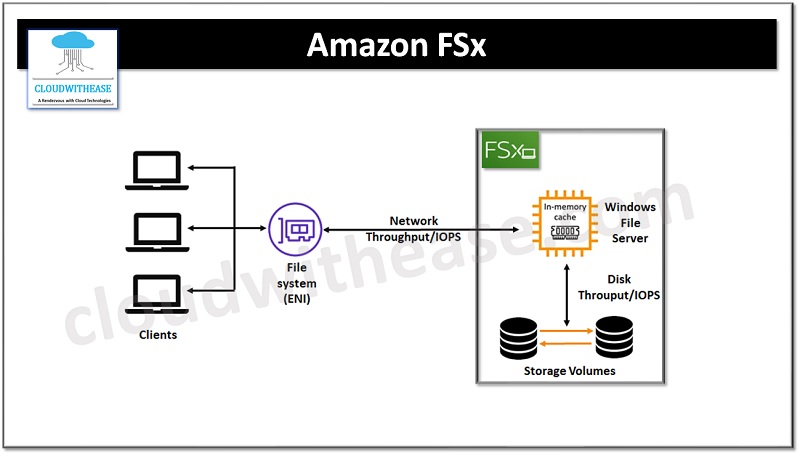
Amazon FSx allows the launch of file systems in the cloud, and supports options such as NetApp ONTAP, OpenZFS, Windows File Server, and Lustre. It is a high performance storage solution with cost savings. It is ideal for machine learning, high performance computing and video processing.
Amazon FSx in windows is a fully managed file storage service with compatibility to SMB protocol used in windows-based applications. For NetApp ONTAP it offers high performance file storage accessible via Linux, Windows, and MacOS compute instances supported with protocols such as NFS, SMB, and iSCSI. Its OpenZFS service is accessible via instances or containers via the NFS protocol.
What is Amazon EFS?
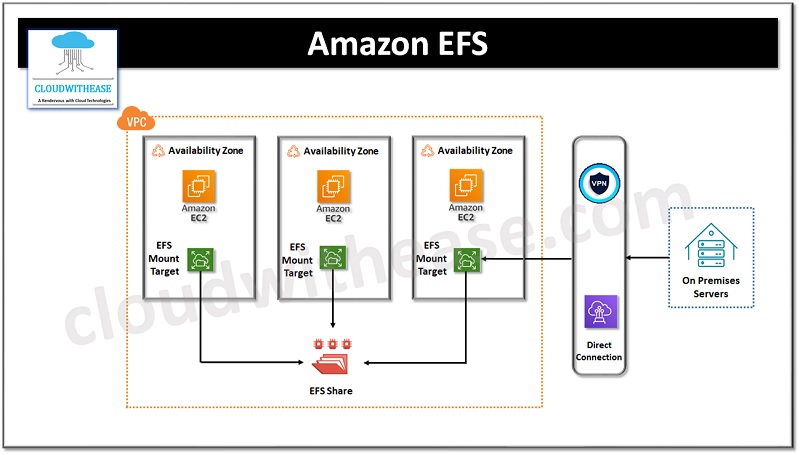
Amazon EFS is an Auto Scalable – Elastic File System which is ideally suited for applications with high workloads which requires a scalable storage and fast output and if workload decreases so as the storage capacity is brought down. EFS can be mounted on AWS services such as EC2 and access it from virtual machines. Ideal use cases for EFS are shared volumes like NAS devices, big data analysis, and any scalable workload.
Secure access is provided using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC). With EFS you pay only for the storage you use so it is a cost-effective solution to manage storage needs.
Key Differences: Amazon FSx vs EFS
The key differences between the two are:
Accessibility
Amazon FSx for Windows is accessible via windows, Linux and MacOS compute instances and devices. Amazon FSx for Lustre is used only by Linux based instances. AWS EFS is accessible via EC2 machines and can be mounted on AWS services.
Interface
FSx has elastic network interface. While, EFS has web and file system interface.
Storage Type
FSx is a file type storage. On the other hand, EFS is an object type storage.
Scalability
In FSx, the storage capacity needs to be increased manually and only every six hours you can do so. EFS automatically scales in storage to handle petabytes of data.
Redundancy
FSx windows can be deployed in multiple AZs or a single AZ. Multi-AZ provides automatic failovers. FSx for Lustre has two deployment options – scratch file systems data is not replicated hence it is not available if server fails whereas persistent file systems data is auto replicated within AZ which is associated with file system. EFS file system object of standard storage is stored redundantly across multiple AZs.
Speed
FSx has low transfer rates and EFS is faster.
Use cases
Common use cases for FSx for Windows are CRM, ERP, custom or .NET applications, home directories, data analytics, media and entertainment workflows, software build environments and Microsoft SQL server. And the common use cases for FSx for Lustre are machine learning, high performance computing (HPC), video processing, financial modelling, genome sequencing and electronic design automation (EDA)
On the other hand, EFS is ideal for applications that require scalability and faster output and sharable workloads such as EC2 instances. Additionally, Big data and analytics workloads, media processing workflows, content management, web servicing and home directories are also the common use cases of EFS.
Encryption
FSx for Windows encrypted file system data and backups at rest using keys managed via AWS KMS. Data in motion uses SMB Kerberos session keys for encryption. FSx for Lustre encrypts file system data and backups at rest using keys managed via AWS KMS and encrypts data in motion when accessed from EC2 supported instances.
EFS gives the ability to encrypt data at rest and in motion. Data at Rest is encrypted using AWS KMS and for data in motion encryption TLS 1.2 is used.
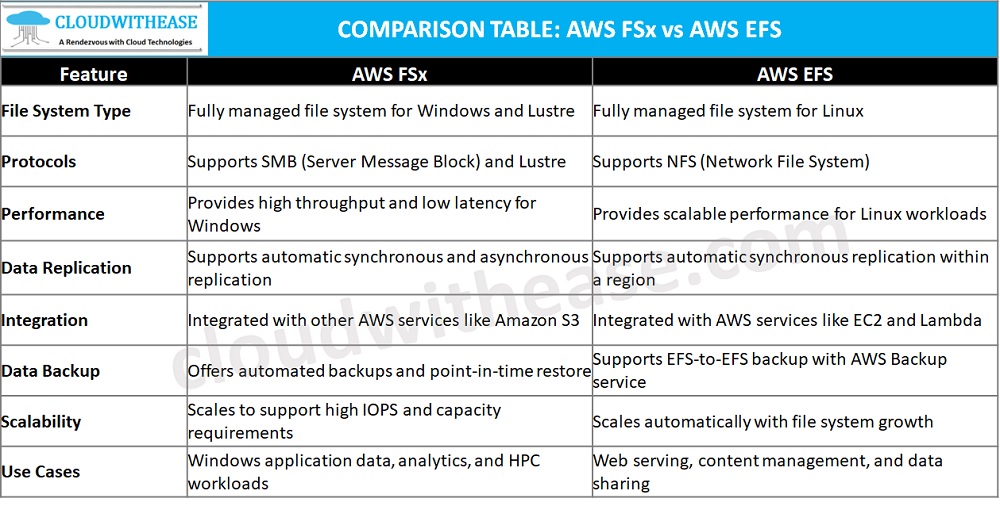
Comparison Table: Amazon FSx vs EFS
Below table summarizes the differences between the two:
Download the comparison table: AWS FSx vs EFS