Table of Contents
As more and more organizations become cloud centric and rely on cloud service providers to host their sensitive data and running applications on their hosting infrastructure, the need to safeguard data from malicious vectors is highly prominent. Encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding data, and ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability on cloud. Apart from security concerns there are compliance and regulatory requirements to store data in encrypted format in cloud environments.
Today we look more in detail about what is cloud encryption, how encryption works in the cloud, key management in cloud, secure data transmission, and types of cloud encryption.
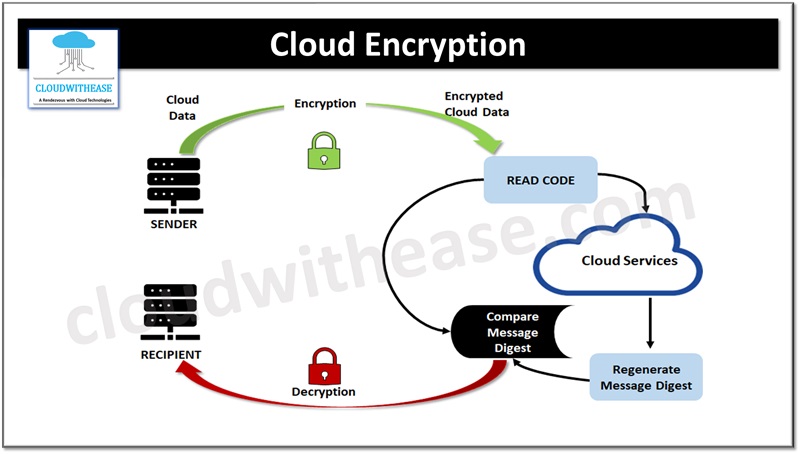
What is Cloud Encryption?
Encryption is a technique which converts data into a code that cannot be used without decoding or decrypting it. Decryption of data is a tough task without access to the key which was used to encrypt it. Data should be encrypted as a best practice both during rest and while in transit or motion or when it is used. In cloud encryption; at rest, in transit and in use, all three are applicable scenarios. If perimeter intrusion controls are breached, encryption is considered the last line of defense to prevent unauthorized access or usage of sensitive personal information. Let’s look more in detail about some key concepts related to cloud encryption.
- Client vs server-side encryption – Data is encrypted using cryptographic algorithms and keys. The encryption can be done at client side or the server side. The client-side encryption is considered more secure as encryption keys are never shared with cloud service providers (CSPs).
- Key management – is pivotal to ensure security of encoded information. Cloud service providers should have strong key management procedures in place to generate, store, pivot and deny or grant access on case-to-case basis.
- Secure data transmissions – During information transmission also encryption applies in cloud. Transport layer protocol (TLS) or Secure attachments layers (SSL) ensure encoded information during transit to eliminate risks of eavesdropping and tampering.
- Compliance and regulatory mandate – Adopting a strong encryption assists organizations and service providers on cloud to meet compliance and regulatory obligations towards information security and its protection.
Advantages of Cloud Encryption
- Confidentiality and data privacy – Cloud encryption ensures that information remains private and secret. Encryption of data before its storage on cloud and while it is transmitted ensures data is not accessed by unauthorized personal cloud provider staff without having appropriate decryption keys to decode data. This ensures information against breaches, insider threats and unapproved access.
- Integrity of data – Encryption protects information from unapproved access and also ensures information is not tempered with. With encryption in place an unapproved party can’t make changes to information without proper decoding keys.
- Compliance and trust – Cloud encryption helps meet regulatory requirements , like GDPR (General Information Security Guideline) in Europe or HIPAA (Health care coverage Versatility and Responsibility Act) in the medical services industry.
- Data transmission security – Data encryption in transit protects data from tempering during its transmission between client and cloud servers. Encryption standards like TLS and SSL establish secure transmission channels to prevent unauthorized access to data in a moving state.
- Multi-tenancy security – In multi-tenancy cloud environments, each tenant data is separately encrypted and secure to ensure accidentally or maliciously one client data is not accessible by another client.
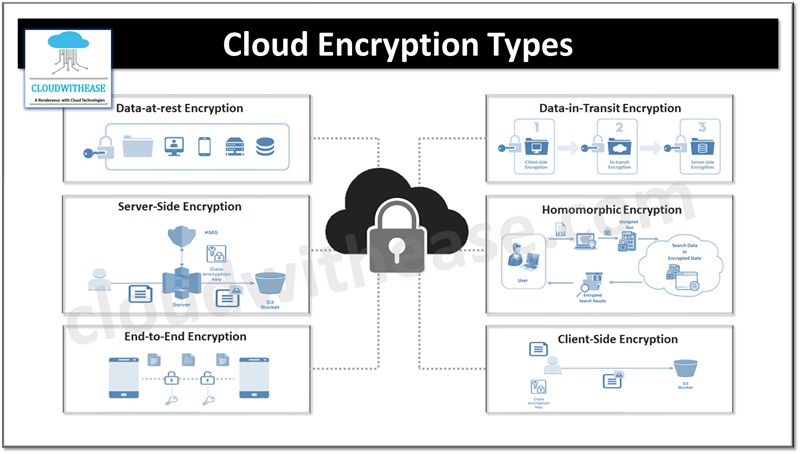
Cloud Encryption Types
There are several types of cloud encryption used to serve different purposes and provide different levels of security. Some of the most common types are described here.
Data-at-rest Encryption
Data-at-rest encryption means encryption data while it is stored in cloud storage. The encryption at rest ensures even if someone gains unauthorized access the information remains encoded and distant without the legitimate decryption keys. Cloud service providers have built-in data-at-rest encryption features in their storage by default.
Data-in-Transit Encryption
Data-in-transit encryption, technique uses TLS and SSL to secure or encode data in motion and establish secure and encrypted communication channels to safeguard from eavesdropping during transit.
Client-Side Encryption
Client-side encryption includes encoding information on the client’s side before being transmitted onto cloud. This approach ensures encryption keys are always in the client’s control, providing an extra layer of safety.
Server-Side Encryption
Server-side encryption happens when information is decrypted after it shows up at the cloud supplier’s servers. The encryption keys reside with cloud provider, which means they have the obligation regarding key administration and its security.
End-to-End Encryption
This type of encryption guarantees that information remains encoded all through its whole lifecycle, from the client-side, during travel, and very still in the cloud.
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption is latest technology in encryption spaces which permits computations or actions on encrypted data without the need to decrypt it. This means that data can be processed in its encrypted form, and only the final results are decrypted.
