Table of Contents
We have seen the evolution of data warehousing over the years. The introduction of cloud computing has brought about significant changes in the data warehousing landscape. One of the popular cloud-based data warehousing solutions is Amazon Web Services (AWS) Redshift. In this article, we will compare AWS Redshift vs traditional data warehousing and determine which is the best option.
What is AWS Redshift?
AWS Redshift is a cloud-based data warehousing service provided by Amazon Web Services. It is a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse solution that enables businesses to analyze data using industry-standard SQL. AWS Redshift is built on top of PostgreSQL, an open-source relational database management system.
AWS Redshift is designed to be scalable, allowing businesses to add or remove nodes as needed to meet their changing data warehousing needs. It is also highly available, with automatic failover capabilities that ensure data is always accessible.
Key Benefits of AWS Redshift
- Scalability: One of the main benefits of AWS Redshift is its scalability. It allows businesses to add or remove nodes as needed, making it easy to scale up or down depending on the amount of data being stored and processed.
- Accessibility: AWS Redshift is also highly available. It has automatic failover capabilities that ensure data is always accessible, even in the event of a node failure.
- Performance: Another key benefit of AWS Redshift is its performance. It is designed to handle petabyte-scale data and can process queries quickly, making it ideal for businesses with large amounts of data.
AWS Redshift Limitations & Challenges
While AWS Redshift has many benefits, it also has some limitations and challenges.
- Pricing Structure: One of the main challenges is its pricing structure. AWS Redshift pricing is based on the number of nodes, which can be expensive for businesses with large amounts of data.
- Complexity: AWS Redshift requires a high level of technical expertise to set up and manage, which can be a challenge for some businesses.
- Functionality: It is primarily designed for data warehousing and does not offer the full range of features provided by traditional data warehousing solutions.
What is Traditional Data Warehousing?
Traditional data warehousing solutions have been around for decades and are typically on-premises solutions. They are designed to store and manage large amounts of data and provide business intelligence and analytics capabilities.
Traditional data warehousing solutions are typically built using relational databases and require a significant amount of hardware and infrastructure to set up and manage.
Advantages of Traditional Data Warehousing
- Flexibility: They can be customized to meet the specific needs of a business and can be integrated with other systems and applications.
- Functionality: Traditional data warehousing solutions also offer a wide range of functionality, including data modeling, data integration, and business intelligence and analytics capabilities.
- Cost-effective: Traditional data warehousing solutions are typically more cost-effective than cloud-based solutions like AWS Redshift, especially for businesses with large amounts of data.
AWS Redshift vs Traditional Data Warehousing
When comparing AWS Redshift with traditional data warehousing solutions, there are several factors to consider, including scalability, availability, performance, functionality, and cost.
- Scalability: AWS Redshift has the edge in terms of scalability. It is designed to be highly scalable and can easily add or remove nodes as needed. Traditional data warehousing solutions can also be scaled, but this typically requires significant hardware and infrastructure investments.
- Availability: Both AWS Redshift and traditional data warehousing solutions are designed to be highly available. However, AWS Redshift has automatic failover capabilities that ensure data is always accessible, even in the event of a node failure.
- Performance: AWS Redshift has the edge here as well. It is designed to handle petabyte-scale data and can process queries quickly, making it ideal for businesses with large amounts of data. Traditional data warehousing solutions can also be high-performing, but this typically requires significant hardware and infrastructure investments.
- Functionality: Traditional data warehousing solutions have the edge. They offer a wide range of functionality, including data modeling, data integration, and business intelligence and analytics capabilities. AWS Redshift is primarily designed for data warehousing and does not offer the full range of features provided by traditional data warehousing solutions.
- Cost: In terms of cost, traditional data warehousing solutions are typically more cost-effective than cloud-based solutions like AWS Redshift, especially for businesses with large amounts of data.
Comparison Table:
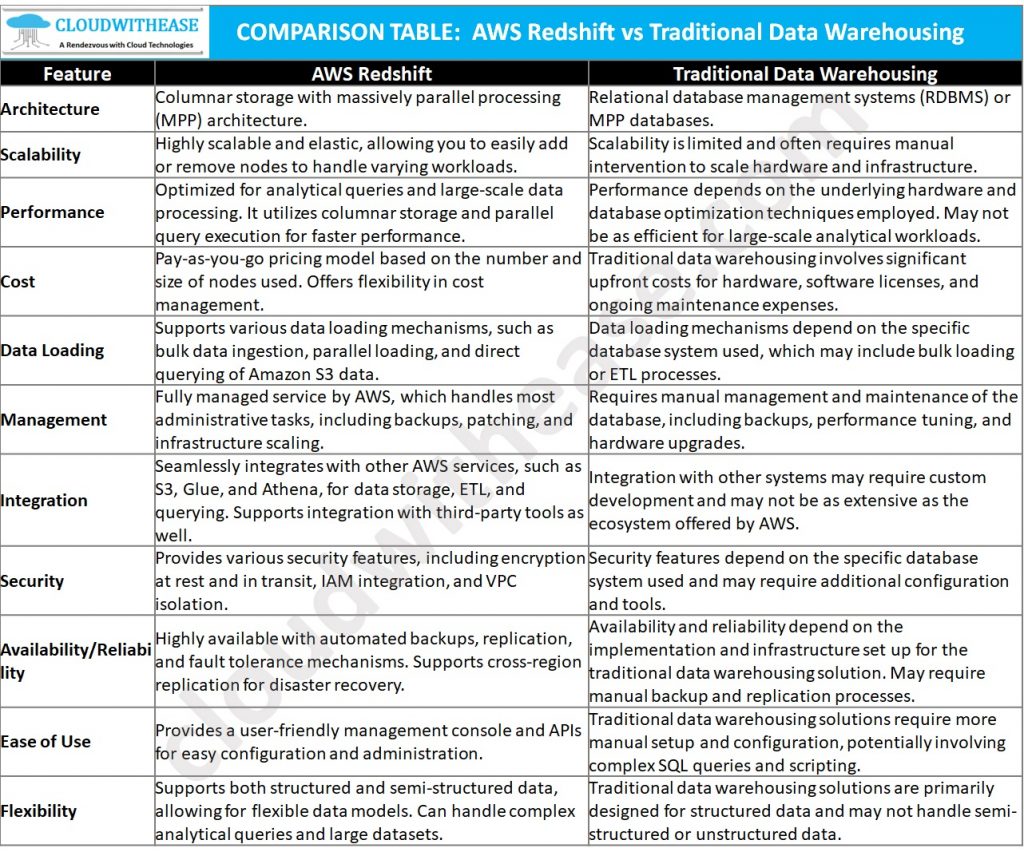
Download the comparison table: AWS Redshift vs Traditional Data Warehousing
How to migrate to AWS Redshift from Traditional Data Warehousing?
Migrating from traditional data warehousing solutions to AWS Redshift can be a complex process. It requires a high level of technical expertise to set up and manage.
- The first step in migrating to AWS Redshift is to evaluate the existing data warehousing solution and determine which data can be migrated. This typically involves identifying the data sources and mapping the data to the AWS Redshift schema.
- Next, the data must be loaded into AWS Redshift. This typically involves using tools like AWS Data Pipeline or AWS Glue to extract the data from the existing data warehousing solution and load it into AWS Redshift.
- Finally, the existing applications and systems must be updated to work with AWS Redshift. This typically involves updating the application code to use the new data sources and modifying the database queries to work with the AWS Redshift schema.
Conclusion
Both options have their advantages and disadvantages. AWS Redshift is highly scalable and high-performing, but can be expensive and has some limitations in terms of functionality. Traditional data warehousing solutions are more cost-effective and offer a wider range of functionality, but require significant hardware and infrastructure investments.
Ultimately, the best option depends on the specific needs of the business. For businesses with large amounts of data and complex data warehousing needs, AWS Redshift may be the best option. For businesses with smaller data sets and simpler data warehousing needs, traditional data warehousing solutions may be the best option.