Table of Contents
Whenever you want to access some public resource on the internet you need to have a routable public IP address to source the traffic from as private IP ranges aren’t routable over the internet. And since the public IPV4 address ranges are limited and have costs associated with them, it isn’t a good idea to have a public IP assigned for all resources that want to go over the internet.
Hence, technologies like NAT (Network Address Translation) have been coined to reduce the public IPs requirement of resources that want to talk to the internet. With NAT a single Public IP address can be used to represent a range of private IPs over the internet by mapping those Private IPs to a single Public IP assigned for NAT.
What is Azure NAT Gateway?
For resources in Azure that require internet access we have a NAT Gateway service to map the outgoing request from internal VNET resources to an external IP address over the internet. NAT services provide mappings for a single IP address, a range of IP addresses defined by an IP Prefix, and a range of ports associated with an IP address.
Azure NAT service can work with
- Standard SKU Public IP address resources or with
- Public IP prefix resources as well
If you use a Public IP address prefix, you can distribute IPs from that range to multiple NAT gateway resources. A flow is created from VNET to Internet & and return traffic is only allowed in response to an active flow. No inbound traffic from the internet can pass through NAT gateway.
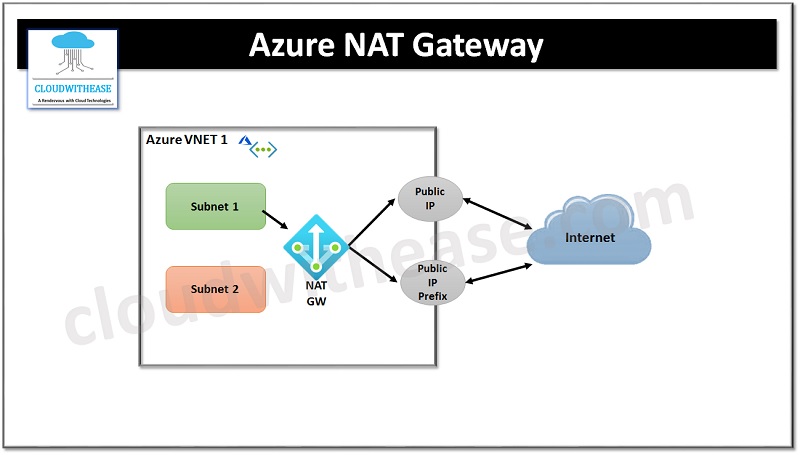
Conceptual Diagram:
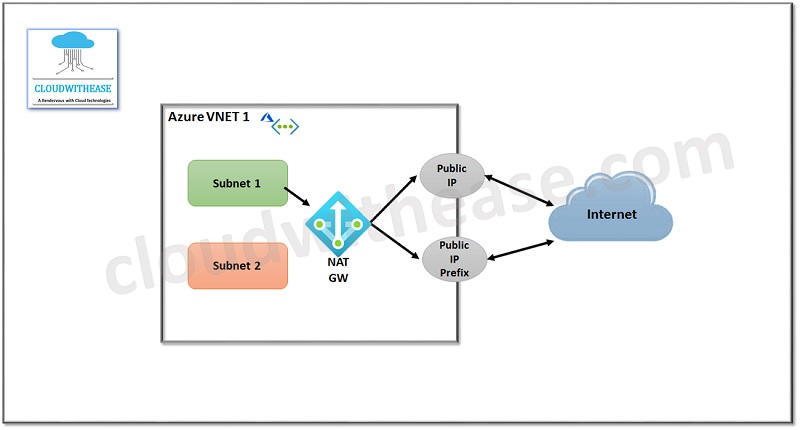
Each subnet within a VNET is associated with the NAT gateway for outbound connectivity. Once a NAT gateway is created you don’t need to use defined routes to route traffic to NAT gateway. NAT gateway takes precedence over other outbound traffic and replaces the default internet next-hop type for the default route in a subnet.
Key Pointers: Azure NAT Gateway
- Each Azure NAT Gateway can support 16 Public IP Addresses.
- In most cases NAT gateway and the public IP address assigned should always be in the same zone.
- Public IPs assigned to NAT gateway cannot be changed.
- However multiple Public IPs can be assigned to a NAT gateway & outbound connection can use any of these Public IPs for connectivity.
- VNET gateway works only with Standard SKU resources i.e., Standard SKU Load Balancer, Standard SKU Public IP.
- A single NAT gateway can be assigned to a single VNET, however within a VNET a NAT gateway can be associated with multiple subnets.
- A single subnet can only have a single NAT gateway associated with it.
- A NAT Gateway can be zonal or in no zone. A no zone NAT gateway means Azure selects a zone for your NAT gateway and there is no guarantee of redundancy.
- In the zonal NAT gateway, you specify the zone for your NAT gateway. Once a zone is selected for NAT gateway at time of creation it cannot be modified later.
- NAT gateway is very much static in nature i.e., it cannot be moved to another region, subscription, resource group.
- NAT Gateway doesn’t work with IPV6
- NAT Gateway doesn’t support fragmentation.