Table of Contents
Cloud computing is widely adopted in all IT environments due to its efficiency and always availability. In the era of cloud computing there is a need for a next generation financial technology to secure electronic cash. Blockchain technology for secure use of electronic cash is widely popular as it helps in communication between peers without involving third parties. It provides security via authentication of peers which share virtual cash, encryption, and hash value generation. According to a global financial industry survey, the market for security based blockchain technology is expected to grow to USD 20 billion by 2024.
Today we look more in detail about how blockchain technology helps financial transactions in cloud computing, its challenges, blockchain solutions in cloud computing etc.
What is Blockchain Security?
Blockchain technology allows all members to keep a ledger of all transaction data and update ledgers to ensure integrity whenever any new transaction happens. Internet and encryption technologies have made it possible to verify transaction reliability and single point of failure arising from third parties have been addressed. The blockchain is a broker free (P2P based) technique, thereby doing away with all transaction fees imposed by third parties.
Ownership of transaction information resides with many people making hacking tough and security expense is saved, transactions are auto approved and recorded by mass participation. System can be easily implemented, connected, and expanded using open source and transaction records are openly accessible making them public and reducing costs incurred on regulatory compliances.
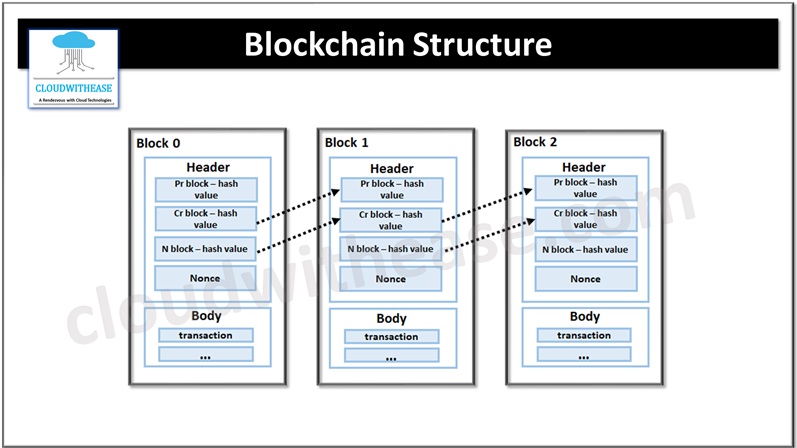
- Blockchain is structured to save data in a form similar to distributed databases and designed to make random manipulation tough as network participants verify and save blockchain. Each block structure comprises a header and body.
- The header contains hash values of previous and current blocks and nonce. The block data is searched using an index method. Block does not contain hash value of next block but it is added as a practice.
- Hash values stored in each peer in block are affected with previous block values, hence it is very difficult to alter or falsify registered data. Data alteration is only possible if 51% peers are hacked at same time which is difficult to achieve in real life scenario.
- Public, key based verification, and hash function both can be decrypted and used in blockchain to provide security.
- The ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) electronic signature algorithm is used to verify digital signatures generated between peers during transactions used to provide no data alternation happened during the transactions.
- The hash function is used for verification of block data containing the transaction information that is not manipulated and to find the nonce value to get a new block to ensure integrity of transaction data during bitcoin transactions.
- The integrity of transaction details is verified using public key-based encryption of hash value of transacted data. Using the root hash value which accumulates hash value of every transaction, enables determination of bitcoin data that was altered since root hash value is modified if value changed in the process.
- Bitcoin is vulnerable to malware infections as it is often traded on widely used devices such as smartphones, Peer systems. But one of the strengths of bitcoin is it is difficult to manipulate and alter the ledger as many peers share the transaction ledger.
Related: Cloud Security vs Traditional IT Security
Blockchain Security: Challenges
Blockchain technology is related to usage of cyber money however the various security issues that might occur in blockchain arrangement related to blockchain agreement, transaction, wallet, and software needs to be addressed.
- Blockchain settlements – Is a sequential connection of generated blocks; it can be divided into two as two latest blocks generate temporarily when two different peers mining answer for generating blocks at the same time. If an attacker has 51% mining capability it can gain control of blockchain and include falsified transactions.
- Transaction security – Scripts used in input and output in programming language different forms can be created. A bitcoin using improperly configured locking script could lead to misuse hence usage verification of script accuracy in transaction is important.
- Wallet security – The bitcoin wallet stores information related to the personal key of the address used for generation of unlocking scripts. Loss of information in wallet could lead to loss of bitcoin therefore bitcoin wallet become target of attack through hacking. To ensure security of Bitcoin wallet usage of multisig for multiple signatures is introduced. Multisig only allows a transaction when there is more than one signature and can be used as the redundant security feature of the wallet.
- Software security – Bitcoin core software is not free from the problem of software malfunction such as bugs. The CVE-2010-5139 vulnerability happened in August 2010 caused by integer overflow, an invalid transaction wherein 0.5 bitcoin was delivered as 184 trillion bitcoin was included in a normal block, and the problem took almost 8 hrs to resolve.
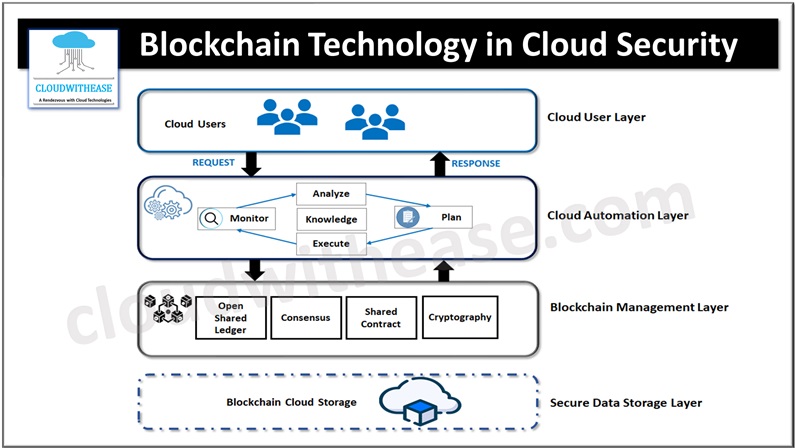
How Blockchain improves Cloud Security?
How Blockchain improves Cloud Security?
- Transparent System: The Blockchain is a transparent system that prevents any suspicious activity in the network. Its sequential storage capability ensures that every transaction is validated, allowing for the establishment of a secure, interconnected, and orderly chain of blocks. This Blockchain-powered cloud storage also generates transaction records to authenticate ownership and identity.
- Decentralization: Blockchain technology divides data into smaller pieces and distributes them across multiple computer networks. This eliminates the need for a central control point. Each computer, or node, holds a complete copy of the record, eliminating the risk of data loss in cloud storage. Even if one or two nodes are accessed incorrectly or corrupted, the entire dataset remains intact. Blockchain also eliminates the necessity for a middleman or “trusted third party.”
- Ensures Data Security: One of the main challenges in cloud storage is the prevention of data tampering and ensuring data security. Blockchain provides a solution by allowing the tracking and backup of transaction history, which confirms any instances of data tampering. By storing hashes for the data blocks, Blockchain enhances the authenticity of the data. Therefore, any tampering with the data will be easily detected.
- Protection against Hackers: Traditional cloud networks are susceptible to hacking, resulting in potential data loss or corruption. Blockchain networks offer a higher level of security. The data within a Blockchain network is encrypted, decentralized, and undergoes verification by all participating nodes. Once a transaction is recorded on the ledger, it becomes extremely challenging to modify it without detection. This is due to the invalidation of signatures and the requirement for confirmation from all nodes. Hacking into a Blockchain network would necessitate simultaneous hacking of all nodes, a task that is currently beyond the capabilities of cyber criminals.

