Table of Contents
Cloud computing has changed drastically the way organizations work and advanced us towards a new technology era. There are many top cloud providers in the market today – Amazon web services, Google cloud, Microsoft Azure, IBM cloud and so on.
Majority of enterprises are now moving towards cloud and multi-cloud environments to harness the power of cloud computing such as reduction in capex costs, reduction in maintenance costs involved in infrastructure, highly available, scalable and secure IT environment.
But what about security of data over the cloud? What features do cloud service providers offer? What security model do they follow?
Today in this article we will look at Cloud security available with three big cloud providers – AWS, Azure and Google cloud platform (GCP), about the shared responsibility model followed in cloud services.
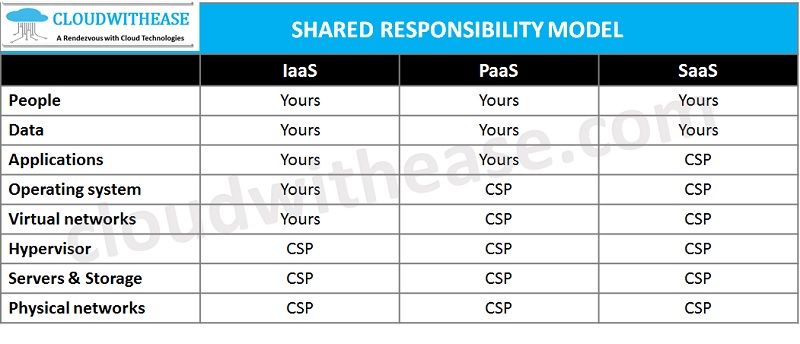
What is Shared Responsibility Model?
Shared responsibility model framework is used to define accountability at cloud provider and organization level based on what is deployed in the cloud. The below table depicts that.
Now we look at how three cloud providers handle shared responsibility models. Approach is almost the same for all three but with some slightly different approaches.
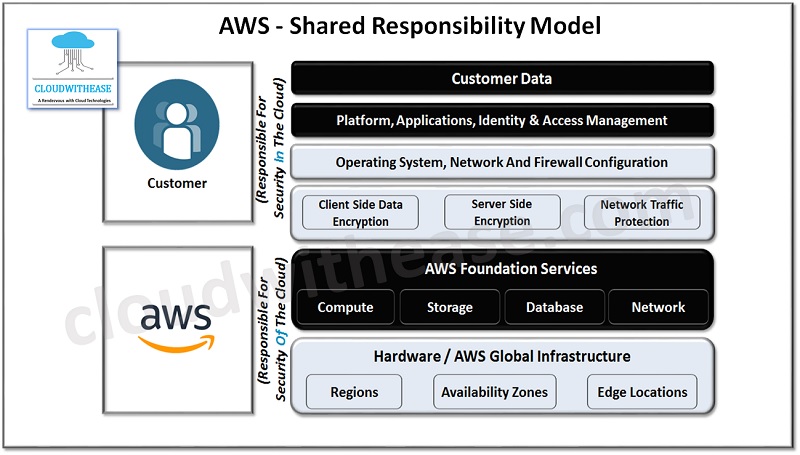
AWS Shared Responsibility Model
In AWS customers are responsible for security in the cloud – their own data, user accounts, applications etc. AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud which includes its underlying hardware within data centres like physical machines, storage and networking components.
AWS IaaS
AWS offers below cloud security features for the IaaS model:
- AWS has Shield for Denial-of-service protection.
- The Secret manager of AWS is used for storing secrets only in addition to the mechanism to store certificates.
- AWS VPN supports point to site and site to site options with site-to-site connections limiting 10 connections per VPN gateway.
AWS SaaS
AWS offers cloud security features in SaaS model:
- Their security assessment service is called Amazon Inspector.
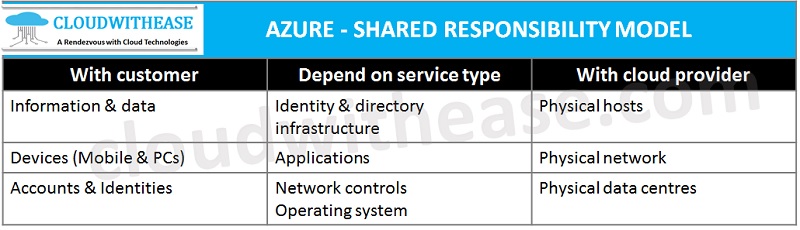
Azure Shared Responsibility Model
In Azure shared responsibility model customers are responsible for information, data and devices such as mobile and systems, user accounts also known as identities.
The second category is more grey area and would depends on cloud model being used or deployed such as Platform as a service (PaaS), Software as a service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a service (IaaS).
Third category is cloud service provider responsibility where provider is wholly and solely responsible for the security be it Platform as a service, Software as a service, infrastructure as a service such as physical infrastructure in data center hosting these services.
Azure IaaS
Azure offers below security features for the IaaS model:
- Distributed Denial of Service known as DDoS protection.
- Azure has a service called key vault which is used to store secrets like credentials and keys and also certificates can be stored here.
- Azure VPN gateway supports point to site and site to site options with site-to-site connection limiting 30 sites to site connections per VPN gateway.
Azure SaaS
Azure offers security features for SaaS model:
- Their security assessment service is called Azure security centre.
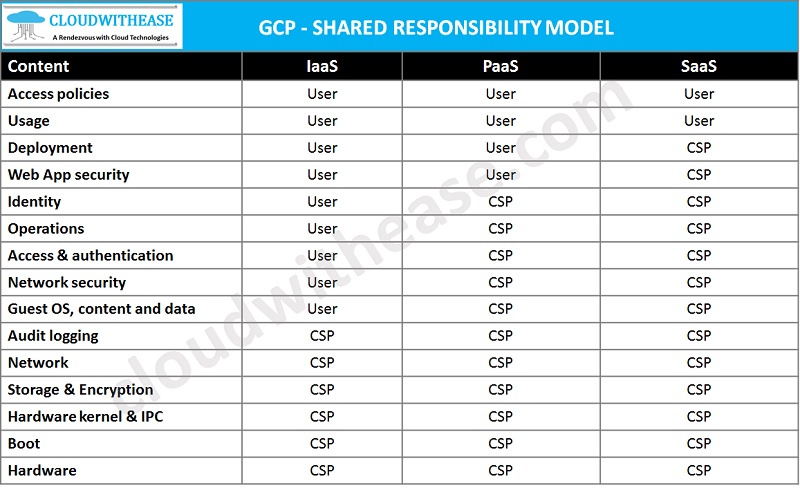
GCP Shared Responsibility Model
Google’s approach to the shared responsibility model is a bit complex in nature. For each instance they specify in detail who is responsible for security.
GCP IaaS
GCP offers below security features for the IaaS model:
- It has Google cloud Armor for denial-of-service protection.
- GCP secret manager provides functionality to store passwords and certificates.
- Google cloud VPN only supports site to site VPN and does not support point to site connections.
GCP SaaS
GCP offers security features for SaaS model:
- Their security assessment service is called Trust and security centre.
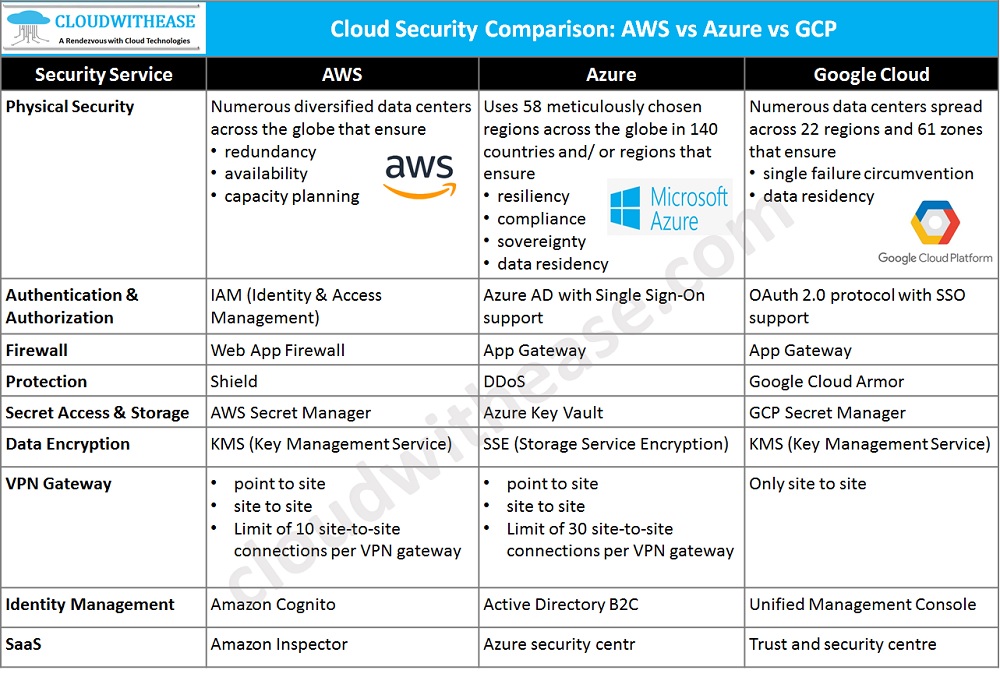
Cloud Security Comparison: AWS vs Azure vs GCP
All three providers offer common security services over PaaS:
- Identity and access management policies,
- Firewall rules inclusive of IP whitelisting
- Encryption in transit using TLS
- Hard drive encryption
Below table summarizes the comparative points between the three major cloud service providers discussed here.