Table of Contents
Cloud providers offer a wide variety of storage options over the cloud to suit different business needs and pricing options. Based on the business requirements customers can choose the right storage option for their IT requirements and align to regulatory and other needs which demand storage of data for specific purposes and specific durations. Amazon AWS, one of the largest cloud service providers offers S3, EBS and EFS type of cloud-based storage options.
In today’s article we understand and compare Amazon AWS storage options – Amazon simple storage service (S3), Amazon Elastic block storage (EBS) and Amazon Elastic file system (EFS), their key differences i.e. EBS vs EFS vs S3 and use cases.
What is EBS
Amazon Elastic block storage (EBS) is for all AWS block storage services over cloud. It allows to store files directly on an EC2 instance so they can be accessed quickly. They can be customized to best suit the needs and support required workload. Based on requirements such as the need is for greater throughput you can choose a throughput optimized HDD EBS volume. For general purpose you can choose EBS general purpose SSD. High performance volume needs EBS provisioned IOPS SSD volume and so on. This works simply like a hard drive working on a computer.
Use Cases for EBS Storage
- Many organizations require cheaper storage options to run their databases. EBS provides relational and NoSQL databases with scalability solutions having low latency performance. Slack is example of one such messaging application which uses EBS to increase performance of database
- Ideal for backups which can be easily uploaded to S3 bucket for convenient and cheaper storage option
What is EFS
EFS allows businesses to share file data simultaneously from multiple EC2 or on premises instances. It is an elastic and serverless service which automatically grows and shrinks as per file storage needs of business without any manual intervention of its provisioning or management. It gives some additional advantages such as dividing content between less frequently and more frequently accessed. Being a native solution to Amazon AWS it works with containers and functions such as EC2 and AWS Lambda.
Use Cases for EFS Storage
- Ideal for machine learning and big data workloads
- Management of content and web applications
What is S3
Being an object storage solution, it offers scalability to shrink or expand to meet demands of growing data storage needs in a cost effective manner. It helps to manage data, ability to control who access what content, data protection against latest threats. Replication of data for increased availability and choose between different storage classes as per the need.
Use Cases for S3 Storage
- High redundancy and availability requirements
- Archival of data for regulatory purposes in cost effective manner
Comparison: EBS vs EFS vs S3
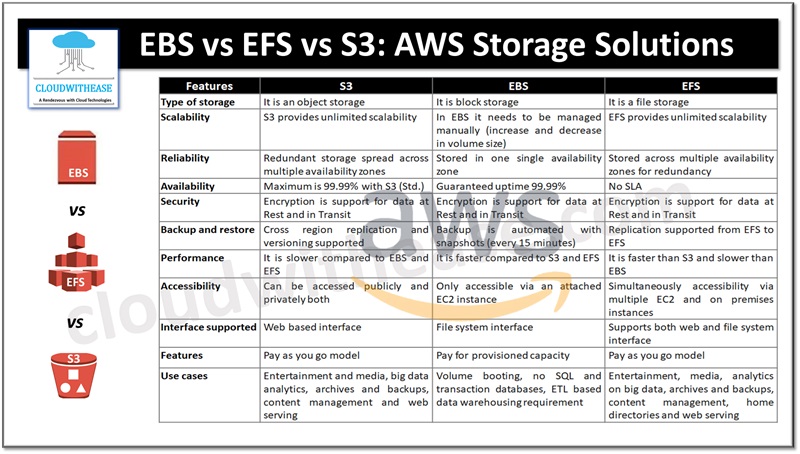
| Features | S3 | EBS | EFS |
| Type of storage | It is an object storage | It is block storage | It is a file storage |
| Scalability | S3 provides unlimited scalability | In EBS it needs to be managed manually (increase and decrease in volume size) | EFS provides unlimited scalability |
| Reliability | Redundant storage spread across multiple availability zones | Stored in one single availability zone | Stored across multiple availability zones for redundancy |
| Availability | Maximum is 99.99% with S3 (Std.) | Guaranteed uptime 99.99% | No SLA |
| Security | Encryption is support for data at Rest and in Transit | Encryption is support for data at Rest and in Transit | Encryption is support for data at Rest and in Transit |
| Backup and restore | Cross region replication and versioning supported | Backup is automated with snapshots (every 15 minutes) | Replication supported from EFS to EFS |
| Performance | It is slower compared to EBS and EFS | It is faster compared to S3 and EFS | It is faster than S3 and slower than EBS |
| Accessibility | Can be accessed publicly and privately both | Only accessible via an attached EC2 instance | Simultaneously accessibility via multiple EC2 and on premises instances |
| Interface supported | Web based interface | File system interface | Supports both web and file system interface |
| Features | Pay as you go model | Pay for provisioned capacity | Pay as you go model |
| Use cases | Entertainment and media, big data analytics, archives and backups, content management and web serving | Volume booting, no SQL and transaction databases, ETL based data warehousing requirement | Entertainment, media, analytics on big data, archives and backups, content management, home directories and web serving |