Table of Contents
The rise of remote work has compelled companies, even those deeply rooted in traditional industries, to embrace Software as a Service (SaaS) and cloud tools for enhanced competitiveness and agility. Modern platforms like Zoom, Slack, and Salesforce have become indispensable for facilitating seamless collaboration among knowledge workers working from diverse locations. However, as organizations transition to cloud-first strategies, a profound shift in cybersecurity practices is evident. Unlike the traditional on-premise security approach where companies retained full control within their data centers, the cloud-first era poses distinctive cybersecurity challenges.
In the past, businesses hosted their applications in proprietary data centers, affording them comprehensive control over their environments and security measures. The advent of cloud computing, however, marks a transformative departure from this paradigm. Cloud services provide a gateway to easily accessible and scalable computing resources via the internet, revolutionizing the way organizations approach data management and information technology.

The traditional cybersecurity model, rooted in safeguarding against unauthorized access, cyber threats, and network compromise, now encounters a new landscape. The cloud-first world demands a paradigm shift, requiring cybersecurity measures to adapt and evolve alongside the dynamic nature of cloud computing. It’s not merely a change in tools; it’s a reimagining of how we fortify our digital ecosystems.
Cloud computing introduces a novel dimension to cybersecurity, one where the emphasis expands beyond traditional perimeters. The challenge lies in securing data that transcends physical boundaries and exists in a virtual realm. As companies leverage the benefits of cloud infrastructure—scalability, flexibility, and remote accessibility—they concurrently grapple with safeguarding sensitive information from ever-evolving cyber threats.
Yet, there’s an opportunity in this transformation. The integration of traditional cybersecurity disciplines with the cloud-first approach presents a powerful synergy. By combining the diligence of safeguarding against unauthorized access and cyber threats with the innovative capabilities of cloud computing, organizations can forge a resilient cybersecurity framework.
In the unfolding narrative of how cloud computing is changing cybersecurity, this synergy represents not just a necessity but a strategic advantage. It allows businesses to harness the transformative potential of the cloud while fortifying their digital landscapes against the evolving threat landscape. In this dynamic interplay between cloud computing and cybersecurity, a new era emerges—one where security is not a hindrance but an enabler of innovation and digital progress.
Cloud Computing & Cybersecurity
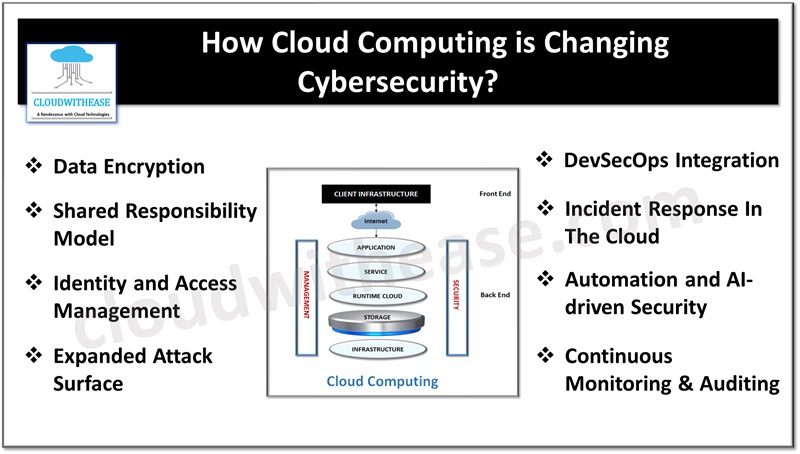
Expanded Attack Surface
Cloud computing expands the attack surface by introducing a virtual and dynamic environment. Unlike traditional on-premise systems with fixed boundaries, cloud infrastructures are scalable, providing flexibility for resource allocation. This dynamic nature creates new entry points for potential cyber threats. As organizations adopt cloud services, it becomes imperative to employ robust security measures that adapt to the fluidity of cloud-based architectures.
Shared Responsibility Model
The shift to cloud brings a shared responsibility model, where cloud service providers (CSPs) manage the security of the cloud infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud. This dynamic necessitates a clear understanding of the division of responsibilities, requiring organizations to fortify their applications and data against potential vulnerabilities, ensuring a cohesive security strategy.
Identity and Access Management
Cloud computing underscores the criticality of identity and access management. With employees accessing cloud resources from various locations and devices, the traditional perimeter-based security approach is insufficient. IAM becomes central, demanding comprehensive strategies for authentication, authorization, and access control. Multi Factor authentication (MFA) and robust identity verification protocols are essential components to thwart unauthorized access attempts.
Related: Comparing IAM Services in AWS, Azure & Google Cloud
Data Encryption
The prevalence of data transmission and storage in the cloud necessitates a heightened focus on data encryption. Organizations must implement robust encryption protocols for data both in transit and at rest. This mitigates the risk of unauthorized interception during transmission and ensures that even if data is compromised, it remains indecipherable without proper decryption keys.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Cloud computing introduces a continuous monitoring paradigm. Traditional periodic security audits are supplanted by real-time monitoring and auditing capabilities offered by cloud platforms. This allows organizations to promptly detect and respond to security incidents, enhancing their ability to address vulnerabilities swiftly and minimize potential damages.
Automation and AI-driven Security
The scalability of cloud resources demands automation in security processes. Cloud platforms leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and predict potential security threats. Automated responses to security incidents enable organizations to respond in real-time, enhancing their ability to combat sophisticated cyber-attacks.
DevSecOps Integration
Cloud computing aligns seamlessly with the DevSecOps philosophy, integrating security practices into the development and operational processes. This ensures that security is not an afterthought but an integral part of the entire software development lifecycle. DevSecOps fosters a culture of proactive security measures, enabling organizations to identify and rectify vulnerabilities early in the development process.
Related: How Can DevSecOps Improve Cloud Security?
Incident Response In The Cloud
Cloud computing necessitates a redefined incident response strategy. The traditional approach, designed for on-premise environments, may not be effective in the cloud. Organizations must develop cloud-specific incident response plans, considering factors such as shared responsibility models, data localization, and the rapid scalability of cloud resources. This ensures a coordinated and effective response to security incidents in the dynamic cloud environment.
Conclusion
As organizations transition to cloud-first strategies, the dynamic nature of virtual environments introduces new complexities and vulnerabilities. Not everyone approaching these digital realms has benevolent intentions. Cyber threats, ranging from data breaches to sophisticated attacks, are ubiquitous, emphasizing the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures.
In this interconnected and interdependent ecosystem, where the cloud revolutionizes the way we store, process, and access data, the stakes are higher than ever. Security is not just a technicality but a strategic necessity, safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring the integrity of digital landscapes.
The transformative trends in cloud computing underscore the urgency for organizations to stay vigilant, adapt their security postures, and foster a culture of cyber resilience. In a world where innovation and connectivity thrive, the pursuit of safety becomes paramount, ensuring that the potential benefits of cloud computing are harnessed without compromising the security and trust that underpin our digital future.