Table of Contents
As more and more organizations are adopting cloud-based architectures to run their businesses, the common challenges faced by them is how to secure and govern their sensitive data in the new cloud environments. Major cloud provider Google is accredited by KPMG LLP as a Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC) solution. This architecture includes Google cloud BigQuery and Dataplex data catalogue which is validated against CDMC’s controls framework and can be adopted by existing Google or new customers for a secure way to migrate their sensitive data to cloud with greater ease and confidentiality.
Today we look more in detail about Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC) architecture, who should be using it, its architecture, and benefits.
What is Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC)?
EDM council had developed and published The Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC) framework. This provides a set of data management capabilities, standards, and best practices to secure cloud environments. The contributors to this framework are large organizations across regulatory industries, cloud service providers, technology service organizations and audit advisory firms.
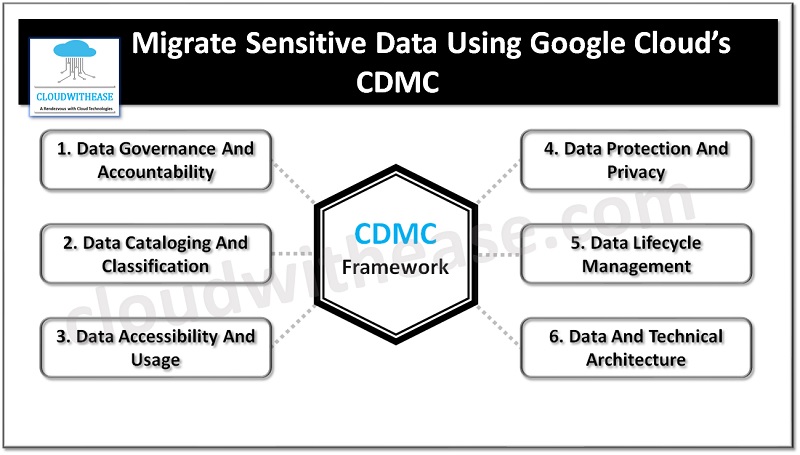
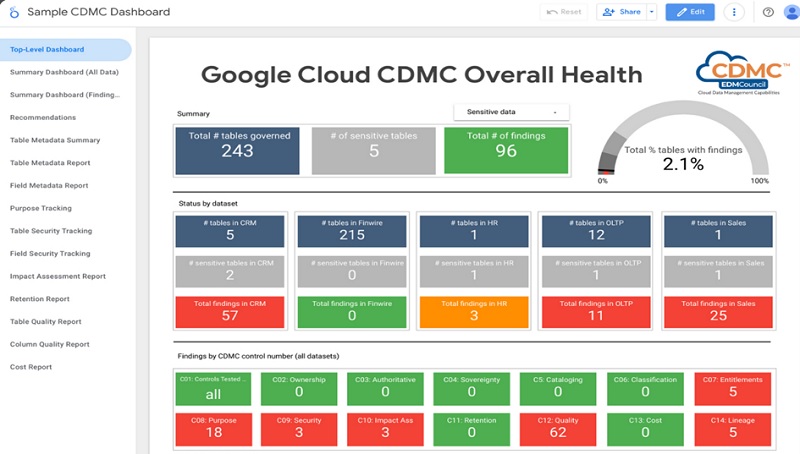
The EDM council data management assessment framework includes 14 key controls and its corresponding assessment procedures which are used to validate sensitive data management. Customer data assets classification with tagged metadata, lifecycle management, and reporting dashboard proactively scans and reports any misconfigurations and issues from a single interface.
Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC) has 6 components, 14 capabilities , and 37 sub capabilities to provide guidance on sensitive data protection in a cloud or hybrid cloud environments.
Adherence to CDMC
Organizations which are involved in handling sensitive data, personal data, regulatory data in cloud, hybrid cloud environments should be primarily concerned on using Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC) framework. The data comprising but not limited to –
- Sensitive personal information (SPI) and Personal information (PI)
- Personally identifiable information (PII)
- Customer identifiable information (CII)
- Material Nonpublic Information (MNPI) and nonpublic information (NPI)
- Sensitive Health information stored manually or in electronic format (PHI / e-PHI)
- ‘Highly restricted’ or ‘Highly confidential’ or any other information with sensitivity classifications
- Critical data used for regulatory reporting
- Licenses related data
Architecture: CDMC
The architecture of Cloud Data Management Capabilities (CDMC) is a combination of a host of Google services with built-in capabilities of platform and data protection services for large data volume.
- BigQuery – Fully managed serverless data warehouse to enable scalable data analysis in large volume (Petabytes).
- Dataplex data catalogue – is fully managed highly scalable discovery of data and metadata management via built-in feature of data lineage.
- Cloud data loss prevention (CDLP)- tools for classification and masking of sensitive data.
- VPC service controls – To mitigate data exfiltration risks in Google cloud resources with perimeter security.
- Looker studio – sample dashboard for visualization of overall health of cloud environment.
- Secure Data warehouse blueprint – Data governance practices while creation, deployment, and operations of data warehouse in Google cloud.
- Tag engine – automation of the process of creation and populating metadata tags in catalogue of data.
Key Controls for Seamless Cloud Data Migration
Let’s look in brief about key controls for seamless cloud data migration and its management.
Identification of Data Assets and Ensuring Security Posture
Data assets are core components of organization secure posture as they are the prime target for cloud data breaches. Robust security posture entails having a controlled inventory of all managed and unmanaged data assets, catalogued as per their residency, ownership, and lineage. A well-maintained data asset catalogue allows security teams to define adequate security controls for sensitive data.
Sensitive Data Discovery, Classification & Data Cataloging
Data privacy and security strategy revolve around trio of data discovery, its classification and cataloging. Migrating from on premises to cloud involves finding and cataloging data assets, the next step is to locate Personally Identifiable Information (PII) , sensitive personal information (SPI) stored on discovered data assets. An effective data discovery is the one which takes care of unstructured data spread across spreadsheets, emails etc.
Data discovery leads to data classification phase where all sensitive data is labelled according to its security and privacy labelling. The security labelling ensures safe and secure access to data and privacy labelling ensures finding correct data, responding to data subject’s requests, right to erase, right to be forgotten, right to inform, or any other rights under GDPR or any other regulations.
Governance of Data Sovereignty & Cross Border Movements
Many global data protection regulations govern data sovereignty and cross border movements which mandate to keep track of all cross-border movement of data, robust security measures for data in transit, Jurisdictions apply to sensitive data as per regulatory standards.
Monitoring Access to Sensitive Data
Access to data and its governance is next stage post discovery , cataloging, classification. Business roles associated with the sensitive data allows to manage and govern better regulation over who and why users need access to data. Role based access controls define access controls as per least privilege principle.