Table of Contents
Cloud computing is based on virtualization of everything required for computing from servers, storage, databases, network components, Applications etc. Cloud computing lets us perform a variety of functions with increased scalability, agility, and security. There are many cloud computing providers currently giving top notch services in the market such as Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, Alibaba, Oracle cloud etc.
This article will talk about Oracle cloud service from Oracle, its primary features, advantages, and limitations, use cases etc.
Introduction to Oracle Cloud
Oracle cloud platform is cloud computing platform from Oracle incorporation. It offers platform as a service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and Software as a service (SaaS) model of computing. It is used to perform tasks such as migrating applications from on premises to cloud, management of development environment, optimization of connection performance etc.
Features of Oracle Cloud
- Oracle cloud offers several tools for building, integrating, monitoring, and securing applications
- Oracle infrastructure supports various languages such as Java, Ruby, PHP, Node.js etc.
- Integration with developer tools such as Docker, DevOps tools etc.
- Unparallelled integration in cloud models as well as on premises platforms
- Maximum IT return on investments
- Customized virtual cloud networks, firewalls, and IP addresses for secure support to private networks
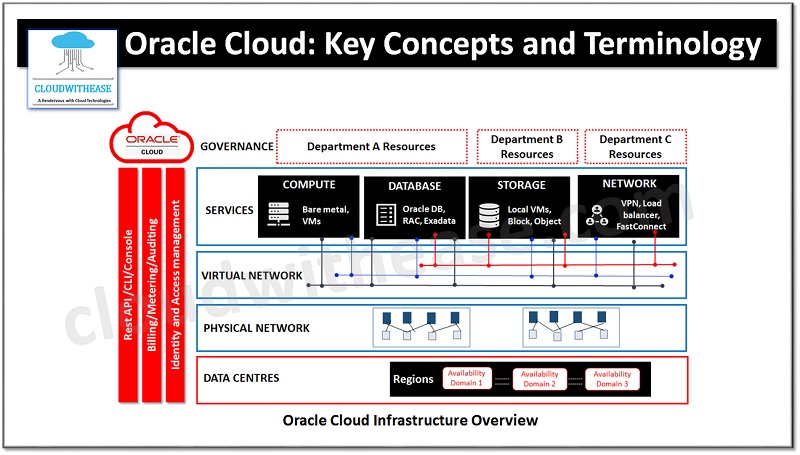
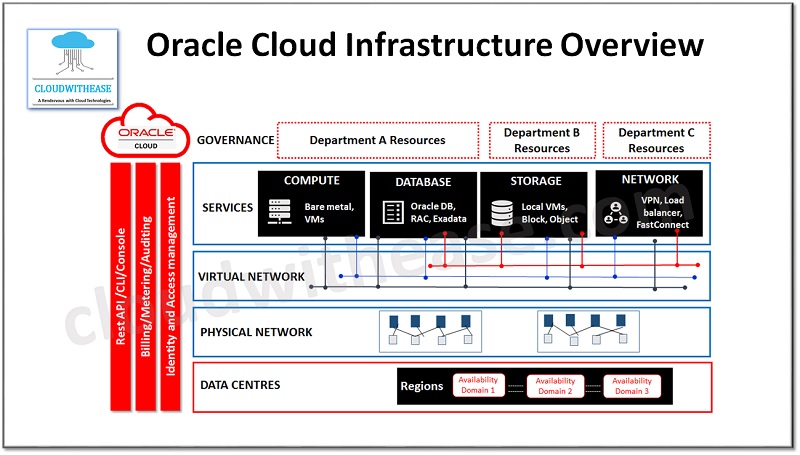
Oracle Cloud: Key Concepts and Terminology
In this section we will look at Oracle cloud key concepts and some information about the terminology being used.
Bare Metal Host
Oracle cloud infrastructure gives facility to control the physical host or server as bare metal compute instances run directly on bare metal without a hypervisor. It is like managing a physical server and its resources such as CPU, memory, storage, NIC cards etc.
It can be configured to utilize its full capabilities with hardware running in your own data centre and there is no sharing with other tenants.
Regions and Availability Domains
Oracle cloud infrastructure is hosted in regions and availability domains. Region is a local geographic area and availability domains are one or more data centres located within that region. Resources categorization could be region specific or could be availability specific, availability domains work in isolation, fault tolerant and no chance of failing multiple zones together so it offers high availability,
Tenancy
While signing for Oracle cloud infrastructure, a separate tenancy instance will get created for your organization, secure and isolated partition within Oracle cloud infrastructure to create, organize, and administer your own cloud resources.
Compartments
Compartmentalization allows organization and control to access cloud resources. Compartment is a collection of related resources (Like instances, virtual cloud networks, block volumes) etc. which are accessible only by certain groups which have been granted permissions by administrator. It is a logical organization or grouping of resources rather than a physical container.
Oracle creates tenancy and root compartment will hold all your resources, additional compartments can be created within tenancy (root compartment) and its corresponding policies to have controlled access to resources within each compartment.
Virtual Cloud Network
It is a virtual version of a traditional network inclusive of subnets, routing tables, gateways which support your instances to run. Cloud networks reside within a single region but can span across multiple availability zones, subnets can be defined for cloud networks in different availability zones however the subnet itself shall belong to a single availability zone, at least one network of cloud required to be set up before launching an instance.
Cloud network can be configured with an optional internet gateway to handle public traffic and another IPsec VPN which is extend to on premises network
Instance
Instance is a compute host running in cloud (A VM).
Image
Image is template of a virtual hard disk with an installed operating system such as Linux, Windows etc.
Shape
Shape is specific to number of CPUs and amount of memory allocated to an instance
Key Pair
Key pair is an authentication mechanism used in oracle cloud, it comprises a pair of two keys –
- a private key
- a public file key
Public key is uploaded on cloud infrastructure while private key is stored securely in your system. Key pairs can be generated with different specifications such as
- Instance SSH key pair – used to establish secure shell (SSH) connection to an instance.
- API signing key pair – this key pair is in PEM format and used to authenticate when submitting API requests.
Only users who have access to cloud infrastructure using API require this type of key pair.
Block Volume
It is a virtual disk which gives persistent block storage space and used as any physical drive and can be detached from one instance and attached to another instance without losing any data
Object Storage
Object storage is storage architecture which allows the storage and management of data objects. Data files size can go up to 50 GB, data uploaded to object storage can be accessed from anywhere. Data which is not accessed very frequently is stored on object storage such as data backup, file sharing, unstructured data storage such as sensor logs etc.
Bucket
Bucket is a logical container used by object storage to store data and files. A bucket can have unlimited number of objects
Oracle Cloud Identifier
Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCid) is a unique ID assigned to any resource in the cloud and it is included as information in the resource both for console and API.