Table of Contents
Introduction to Private Cloud
The cloud has become an essential platform for modern businesses. The cloud is the future and has advantages of new ways of computing. Cloud computing is enabled by virtualization which is the creation of software defined controlled servers. Cloud computing is ‘storage and accessing data and programs over the internet instead of your computer hard disk’. Cloud computing featured as being most scalable and elastic and delivered as service.
Clouds can be several types: Public, private and Hybrid designed especially for compliance and represent different models of cloud computing environment.
We will learn more in detail about Private cloud, its features and design principles, use cases etc.
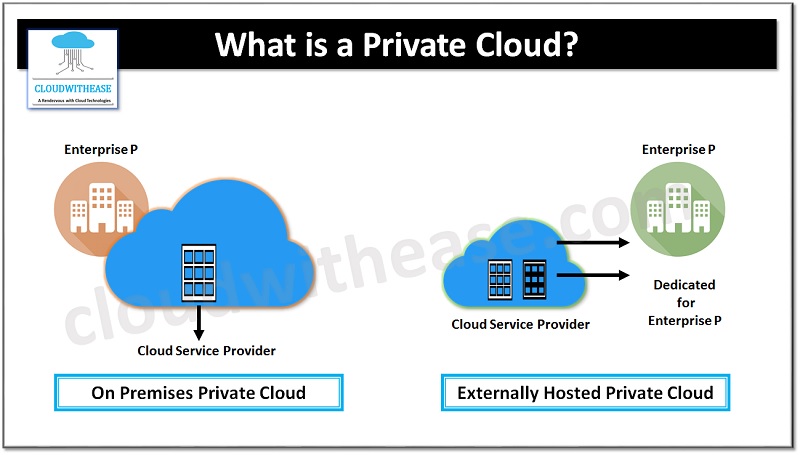
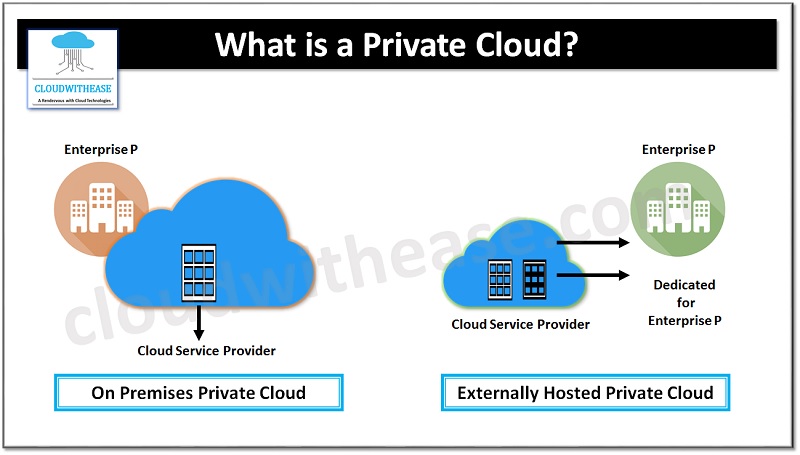
What is a Private Cloud ?
Private cloud is also known as internal cloud or corporate cloud. Private cloud provides computing services to a private internal network (within the organization) and select users. Private clouds provide a high level of security and privacy to data through firewalls and internal hosting. It also ensures that operational and sensitive data is not accessible to third party providers.
In Private Cloud, organizations have their cloud environment in its own data-center and provide self-service access to compute resources for its own organization. Use case scenario for Private cloud when data cannot be exposed on Public Cloud due to legal and security reasons. Legacy or government applications may have such restrictions. Some of the Private Cloud providers are HPE, IBM, VMware, Dell EMC and Oracle.
Private Cloud Framework
Private cloud delivers data and programs from resources which are dedicated to customers. Private clouds are utilized by companies with sensitive data, management, or workload demands. Private clouds are distributed systems which work on private infrastructure and provide the users with dynamic provisioning of systems resources.
Features of Private Cloud
The main benefits of cloud which organizations can attain by running their IT systems in a private Cloud server environment and improve resource utilization, reduction in costs, increased security, regulatory compliance and more flexibility.
Improved resource utilization
Virtualization provides private cloud users improved resource utilization. Workloads can be deployed to a different physical server but as demand changes resources dedicated to the particular server can be adjusted to meet the changing demands of specific applications.
Reduced costs
Flexibility and improved resource utilization help organizations to ensure application performance by reducing costs of getting more out of their servers. A private cloud environment will save money over a traditional on premises environment. Private cloud running on single tenant dedicated VMware is less expensive to businesses.
Increased Security
Private cloud environment provides more robust security features such as robust antivirus and firewall protection, a private cloud runs on certain physical systems, which makes physical security easier to manage. Cloud access is more secure in Private cloud environment due to its private access and secure network links.
Regulatory Compliance
Private cloud environment for organizations having compliance concerns is due to its security and control benefits. Also, service providers help to address significant compliance requirements such as HIPPA and PCI DSS.
More Flexibility
Organizations which are moving from legacy on premises system often have issues in deployment of their workloads to public cloud as it can’t be customized to support any applications.
Pros and Cons of Private Cloud
PROS:
- Dedicated and secure infrastructure which is only accessible by authorized and authenticated users
- Automated and scalable platform to meet unpredictable, transient workloads, avoidance of overprovisioning
- Compliance with security frameworks
- Improved cost-effective model
CONS:
- Initial higher costs and need more IT expertise
- Increased IT and hardware demands without any 3rd party
- Little or no outside support compared to public cloud
Private Cloud: Use Cases
- Extension and consolidation of data centres
- Test and development environments and application development
- Disaster recovery hosting
- Workloads and data with demanding security requirements
- Adherence to Compliance regulations
- Mission-critical business applications