Table of Contents
Both NAT and Proxy are two popular and widely used mechanisms to enable secure access to organizations networks. NAT is used to hide the internal IP addresses from the outside world. NAT let administrators enable use of one set of IP addresses within a Local area network and another set of IP addresses for outside traffic. Proxy acts as a mediator between internal servers holding the resources which clients request for and does its evaluation based on filtering rules and validates requests to provide resource access to clients. In the cloud deployments the traditional working of proxy and NAT is changing however.
Today we look more in detail about traditional Proxy NAT and Cloud NAT mechanisms, their key differences, working and benefits.
What is a Traditional Proxy NAT?
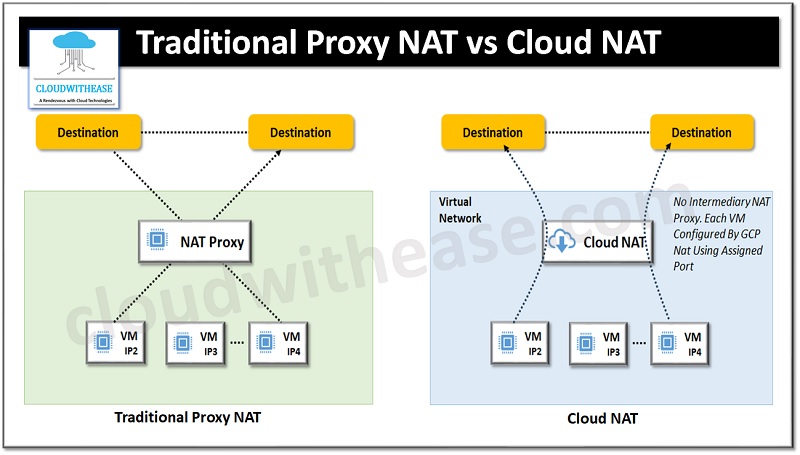
Proxies reside between the end user system and servers and act as an intermediary. All client requests to access resources get routed to proxy and post validation access to resources granted to client based on filtering policies. Proxies work at layer 7 of the OSI model and work at application level such as HTTP or FTP, TFTP etc. proxy provides application-level security. Proxy uses cache to and all requests to the same resources are cached hence proxy brings significant improvement in providing access to resources to intended clients.
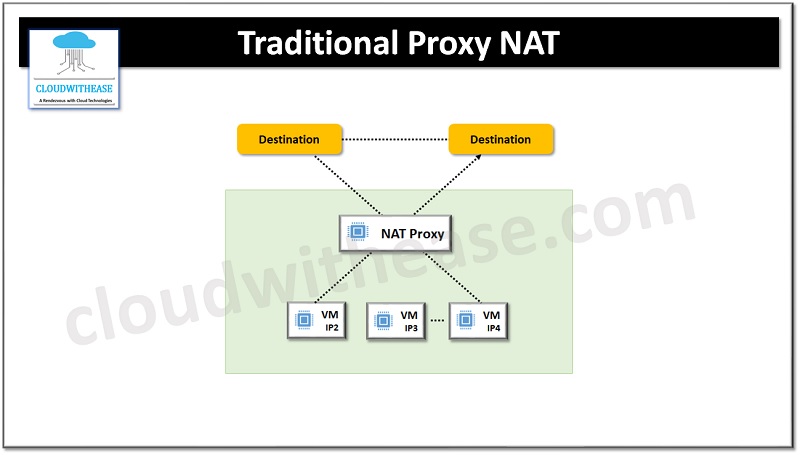
Network address translation or NAT as it is called is a mechanism to change IP address in the header of an IP packet as it travels via a router or switch. NAT allows one set of IP addresses to be assigned for usage for traffic within the local area network (LAN) and another set of IP addresses to be assigned for outside traffic.
What is a Cloud NAT?
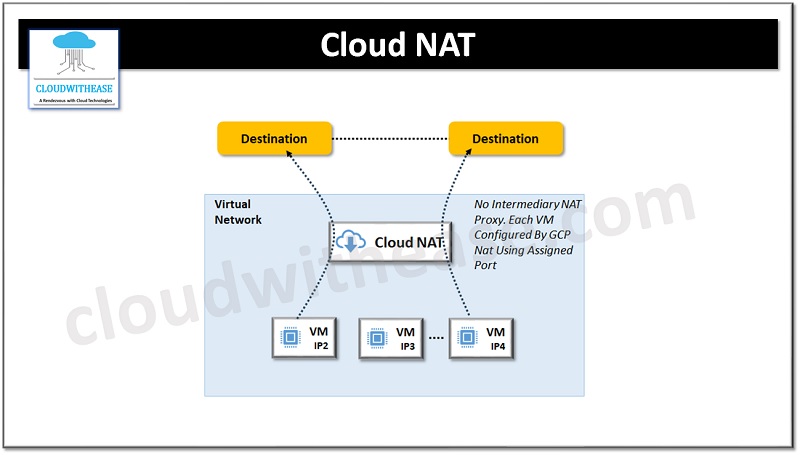
Cloud NAT is network address translation which works as a software defined managed service. It is not based on proxy virtual machines or appliances. It allows virtual machine instances without an external IP address to send outbound packets to the Internet and receive inbound response packets. No inbound connections from the Internet are performed. It works only for virtual machines network interface primary address and alias address and cloud NAT gateway is associated with single VPC network, region, and cloud-based router.
Benefits of Cloud NAT
- No need to assign external IP address individually to virtual machine instances and virtual machine instances can access Internet based on egress traffic rules
- Can perform manual NAT IP assignment and whitelisting by destination service to permit connections from external IP addresses which are known
- It is a distributed, software based managed service and can be configured on a cloud router to provide control plane for NAT with specified configuration parameters
- It can be configured to scale automatically number of NAT IP addresses
- It does not reduce network bandwidth per virtual machine
Traditional Proxy NAT vs Cloud NAT
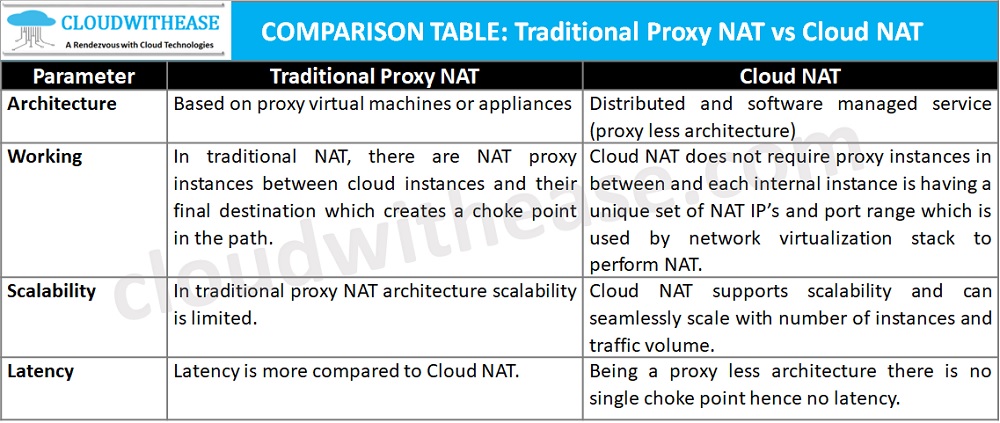
Download the comparison table: Traditional Proxy NAT vs Cloud NAT
FAQs
- What are the use cases for Proxy NAT?
- Load balancing, application-level gateways, content filtering, and other scenarios where more advanced traffic control and manipulation are required.
- What are the use cases for Cloud NAT?
- Cloud NAT is primarily used for outbound internet connectivity for VM instances in a cloud environment. It simplifies the process of ensuring that internal resources can access the internet securely and efficiently.
- Is there a cost difference between Proxy NAT and Cloud NAT?
- The cost structure may vary between cloud providers, but generally, Cloud NAT is a simpler and more cost-effective solution for providing internet access to VM instances. Proxy NAT, with its more advanced features, may be more complex to set up and could involve additional costs.
- Which should I choose, Proxy NAT or Cloud NAT?
- If you need basic outbound internet access for VM instances, Cloud NAT is a straightforward and cost-effective choice. However, if you have more complex network requirements or need to perform deep packet inspection or manipulation, then Proxy NAT may be necessary.
- Can I use both Proxy NAT and Cloud NAT in the same environment?
- It’s possible to use both Proxy NAT and Cloud NAT in the same environment, depending on your specific needs. You might use Cloud NAT for most outbound internet traffic while configuring Proxy NAT for specific, more advanced use cases.
- Do other cloud providers offer services similar to Cloud NAT?
- Yes, other cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, offer similar services to Cloud NAT to enable outbound internet connectivity for their virtual machines.