Table of Contents
In the cloud, establishment of resource boundaries is crucial. This is similar to traditional physical networks where resources boundaries were segregated with physical means, VLANs etc. in cloud this networking service is provided by virtual private connections which enable users to define virtual networks and launching of resources within the boundaries of virtual networks.
It gives full control of various network environments, resources, security and connectivity. It defines how a network communicates across different availability zones or cross regions. Users are given the option to customize network configuration to suit their needs in Amazon virtual private cloud (VPC).
In today’s topic we will learn about Amazon virtual private cloud or VPC, learn about its components, its benefits, its purpose and working.
About Amazon VPC
Amazon VPC creates an isolated virtual network environment in Amazon cloud and it is dedicated to an AWS account. Other AWS resources and services operate inside VPC networks and provide cloud services. AWS VPC is similar to anyone running a physical data center. It is like a traditional TCP/IP network which can be scaled or extended as required.
However, hardware components of physical networks such as switches, routers, VLANs etc. do not exist explicitly in VPC but re-engineered its functionality in cloud software. Using VPC we can quickly set up a virtual network infrastructure that AWS instances can launch into. VPCs define IP addresses, subnets, routing, security and network functionality required by AWS resources.
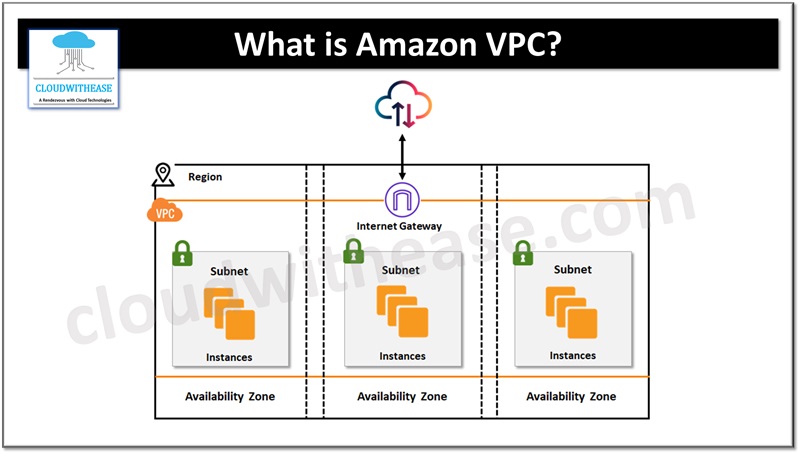
VPCs are created and reside in AWS regions. AWS regions are geo boundaries locations around the world where Amazon has a cluster of its cloud data centers. Amazon creates one default VPC for each account having default subnet, routing tables, security groups and network access control lists. We can modify VPC to use it for cloud configurations or build a new VPC to support services.
Benefits of VPCs
- VPCs can scale and users have total control over network size
- More secure and resources contain cloud infrastructure which is protected by virtual firewalls
- Enable a hybrid cloud environment which can be used as an extension
- Nominal cost due to availability in public cloud
- Easy to create
- Can be connected to a variety of resources such as Internet, VPC accounts and VPN connections etc.
Management of VPCs
VPC management is handled from AWS management console.
AWS management console is a web interface for managing all AWS cloud functions. Amazon CLI provides windows, Linux and Mac commands. AWS software development kit (SDK) provides language specific APIs for VPCs and other services.
Elements of VPC
VPC network service comprises IPV4 and IPV6 address blocks, subnet creation, route tables, Internet connectivity, Elastic IP addresses, Network and subnet security and additional networking services.
VPC IP address range is defined using classless interdomain routing (CDIR) IPV4 and IPV6. Primary and secondary CIDR blocks can be added to VPC. Specifying CIDR blocks from private addresses as specified in RFC 1918 is Amazon recommendation
- Subnet Creation – EC2 instances run inside a designated VPC subnet. Each subnet CIDR contains a subnet of VPC CIDR block. Each subnet isolation of individual traffic from all VPC traffic happens.
- Route Tables – have rules to determine how network traffic is directed inside a VPC and subnets. VPC creates a default route table which is automatically associated with all VPC subnets.
- Internet Connectivity – Each VPC configuration can host one Internet gateway and NAT services using Internet gateway
- Elastic IP Address – Elastic IP addresses are permanently allocated to AWS account and used for public Internet access to an instance, AWS elastic network interface or other services which require public IP addresses
- Network and Subnet Security – VPCs use security groups and provide stateful protection for instances. AWS security groups are virtual firewalls.
- Additional Network Services – provide other common network services such as virtual private networks, VPC peering, gateways, mirror sessions etc.
