Table of Contents
As more and more organizations are adopting cloud for their business operations. There are concerns around security of organization and customer data hosted on cloud. Business requires cloud security architecture to assess how to reduce exposure to cyber risks and threats in cloud use and get insigne into compliance, threat exposure, and overall security.
Today we look more in detail about cloud security architecture, what are key elements of cloud security architecture, cloud security architecture types and principles etc.
Introduction to Cloud Security Architecture
Cloud security architecture is often called cloud computing security architecture. It consists of security layers, design and structure of infrastructure, tools, software, platform, and best practices adopted within a cloud security solution. A cloud security architecture provides a visual and written model to establish how to secure and configure activities and operations in cloud; methods and controls in place for protection of applications, data; approach towards visibility in compliance, threats, and overall security posture.
Processes documented and implemented to instil security principles in coding, development, and operations. Policies and governance to meet standards of security and compliance including physical security infrastructure components.
Key Elements
While developing cloud security architecture we need to include several critical elements:
- Each layer to be secured
- Components management in centralized manner
- Resilient and redundant design considerations
- Scalable and elastic
- Sizing deployment storage
- Notifications and alerts provision
- Standardization and automation across cloud
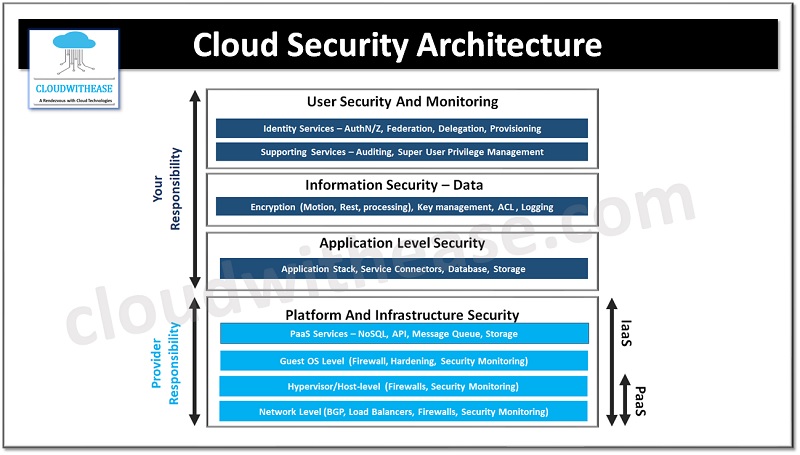
Shared Responsibility: Cloud Service Models
The cloud service models define the cloud security architecture as per applicability. Organizations offering cloud services follow a shared responsibility model as per cloud service model – Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), Platform as a service (PaaS) and Software as a service (SaaS).
Cloud service provider is responsible for security of cloud components required to operate cloud service (computing, software, storage, networking, database, hardware, and infrastructure etc.). The client is responsible for data and information protection which is stored on cloud, as well as who all will have access to that data; however, responsibilities will vary depending on cloud service model.
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) – In this kind of service model in cloud customer is responsible for security of whatever is installed on the infrastructure
- Platform as a service (PaaS) – Application configuration, permissions management and security within application implementation is customer responsibility in this model.
- Software as a service (SaaS) – Customer is responsible for security components to access software, identity management, customer network security and so on.
Principles of Cloud Security Architecture
Let’s look at key principles we need to focus on while defining cloud security architecture as under:
- Identification – Overall cloud resource repository knowledge involving users, assets, business environment, policies, vulnerabilities, threats, risk management strategies which exist
- Controls for security – Parameters and policies implemented across users, assets, data, and infrastructure to manage overall security posture.
- Security by design – Standardized and repeated deployment of common use cases with security controls, standards, and audit requirements.
- Compliance – Integration of industry standard and regulatory standards into cloud architecture to meet the requirements.
- Perimeter Security – Management of connection points between corporate networks and public / external networks.
- Segmentation – To prevent lateral movement of attackers in cloud network segregation of sections.
- User Identity and Access Management – Visibility, understanding, and control on all users which have access to cloud assets. Access, permissions, and protocol enforcement.
- Data Encryption – Data at Rest and data in motion is encrypted to minimize breach impact.
- Automation – Rapid security and configuration provisioning and quick threat detection.
- Logging and Monitoring – activities are captured and monitored related to all connected systems and cloud-based services to ensure operations visibility, compliance, and early detection of threats.
- Visibility in Multi-cloud – Bring visibility in multiple cloud deployments by incorporating tools and processes.
- Flexibility in Design – Agility in architecture design to develop and incorporate new components and solutions without compromising security.
