Table of Contents
Todays’ business landscapes demand performance, flexibility, agility, scalability and off course availability and resiliency. The disasters be it natural or man made can cause disruptions in operations and pose a major threat to availability of critical information and data required business to function seamlessly. There are several replication technologies adopted by organizations to maintain resiliency of business operations in the event of disaster.
Today we look more in detail about how Persistent disk asynchronous replication enables disaster recovery for cloud workloads, how technology works, its benefits and use cases.
What is Persistent Disk Asynchronous Replication?
Persistent disk Asynchronous replication enables disaster recovery for cloud workloads. This performs replication of data between Google cloud regions and maintains (Sub-1) minute recovery point objective (RPO) and lower recovery time objective (RTO). Replication is managed with API calls – VM agents are not required here and there is no dedicated replication performed between virtual machines, there are no limitations of the guest operating system and performance overheads are negligible on the workloads.
Persistent disk Asynchronous replication operates at block infrastructure level and provides a common and fast infrastructure foundation to support disaster recovery capabilities. It can be combined with other forms of data protection such as disk cloning, regional – Synchronous replicated disks, and VM snapshots. Replication is performed between the primary disk in the region to the secondary disk in the secondary region.
Persistent disk Asynchronous replication provides a solid foundation to support infrastructure-based recovery from disasters and help to comply with regulatory requirements for low RTO/ RPO protection of data. Persistent disk Asynchronous replication supports full lifecycle of disaster recovery including – testing, fallback and failover of disaster recovery.
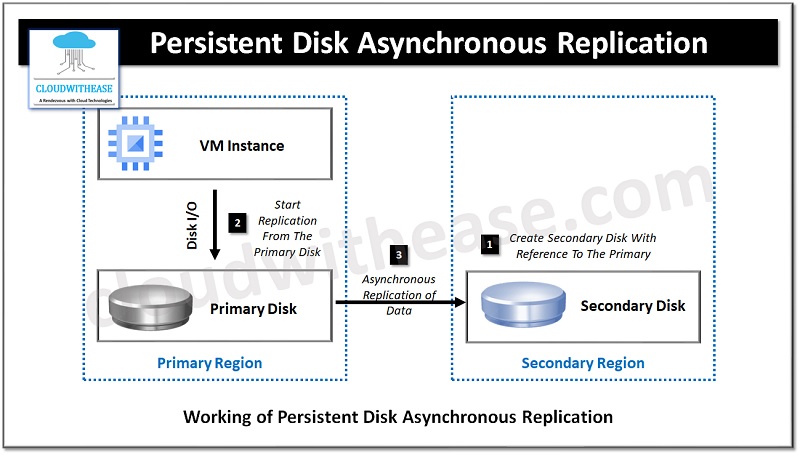
How does Persistent Disk Asynchronous Replication work?
Persistent disk Asynchronous replication can be enabled on existing persistent disks with two API calls –
- gcloud or
- Google cloud console.
Step-by-Step description:
- To start replication the first step is to create a blank disk in the secondary region linking it to persistent disk in the primary region which requires protection.
- Once a link is established, start replication from primary disk to secondary disk. Data replication happens automatically and typically RPO achieved is less than one minute which depends on disk change rate.
- Networks do not require reconfiguration to use Persistent disk Asynchronous replication. Once Persistent disk Asynchronous replication is up and running using cloud monitoring, we can observe the time since last replication and network bytes transmitted.
- Operations teams are responsible to initiate a failover. To initiate failover, replication needs to be stopped between the disks and secondary disk to be attached to VMs in the primary region and this can be achieved in a couple of minutes.
- To restore back to the primary region, post previous failure, new replication pair need to be created and linked to the primary region for workload fallback.
- Replication enablement among data centers in different regions lets you create resilient data replicas which provide protection against local disruptions resulting from natural or man-made disasters.
Persistent Disk Asynchronous Replication Techniques to Achieve Redundancy
- Consistent groups for complex stateful workloads – Consistency groups provide coordinated management of dependent data across disks and VM instances. With consistency groups Persistent disk Asynchronous replication provides simultaneous and atomic data replication with auto synching the replication period across all disks in a consistent group. Data consistency is maintained between primary and secondary disks to support workload recovery when disaster strikes.
- Disaster recovery testing – To test recovery procedures efficiency and ensure they will work in actual disaster scenarios – tests to be performed periodically in secondary regions. This can be achieved without disconnecting Persistent disk Asynchronous replication by using bulk-cloning feature on secondary disks within a consistency group even when new data is getting received by disks.
- High availability and Disaster recovery – Regional persistent disks (Regional PD) and Persistent disk Asynchronous replication work together to provide high availability and disaster recovery. Regional PD can be configured as a primary or secondary async disk and works in combination with a zonal disk in primary or secondary region. When an outage happens in one region in the primary zone having regional PD is configured, the disk still continues to replicate to the healthy zone in the secondary region. Persistent disk Asynchronous replication is established between two distinct disks while Regional PD is actually a single disk which stores data in two zones and it is attached to two zones.
- Posture enhancement for High availability and Disaster recovery – Leveraging Persistent disk Asynchronous replication and consistency groups business gains the agility and redundancy which is required for maintaining business robustness.
