Table of Contents
Enterprises might adopt a hybrid cloud architecture to support business. A hybrid cloud is an IT architecture that integrates public cloud, private cloud, and on-premises infrastructure. Sensitive data may reside with on premises setup and cloud setup is used to dynamically scale up to handle workload peaks.
But this blending of public, private and on premises setup comes with its own security challenges. Data and applications spread across multiple hosting environments, their access management, monitoring and consistent security controls across become a complex task to manage.
Hybrid cloud environments require a holistic approach to secure data and applications, manage identities across private and public ecosystems, very strong identity management, clear and concise policies and threat detection across all environments.
In this article we will learn more in detail about hybrid cloud security, hybrid cloud security architecture, its key components and common challenges.
Understanding Hybrid Cloud Security
Hybrid cloud security refers to a holistic approach towards protection of cloud, on premise assets, cloud and legacy applications, systems by enabling required processes and tools.
A strong hybrid security architecture requires next generation firewalls (NGFW), centralized management of security settings and security tools which can work across hybrid cloud environments.
Hybrid Cloud Security Architecture
The hybrid cloud security architecture requires multiple-layers of defense by deploying perimeter protection with cloud and on premises firewalls. In figure 1 a high-level hybrid cloud security architecture is depicted showing how physical and virtual firewalls are placed strategically for workload protection across environments.
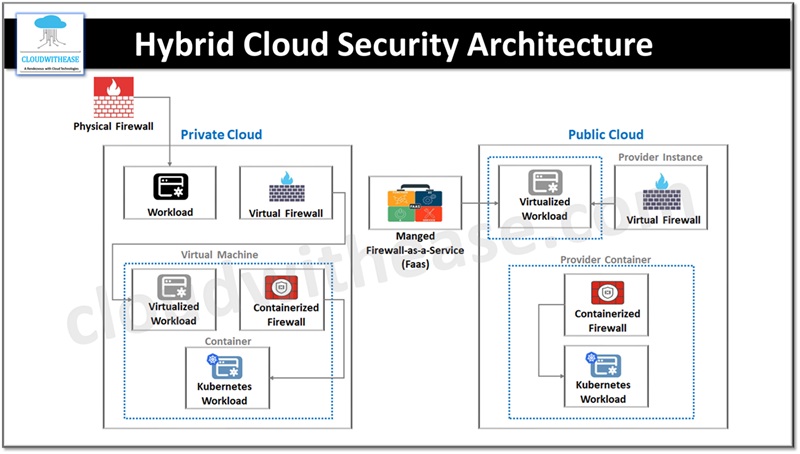
Securing Private Cloud
In a private cloud the entire control lies with the organization. And a typical security layer in a private cloud comprises a physical firewall, virtual firewall and container firewall.
- Physical firewall is deployed for perimeter security and ensure protection from external threats
- Virtual firewall is installed on virtual machines to protect virtual workloads
- A container firewall is installed to protect container applications they inspect and secure east-west or internal traffic in containers.
Securing Public Cloud
Public cloud environments such as Azure, AWS, Google etc. have shared security architecture.
- Managed firewalls (Firewall as service or FaaS) is provided by cloud service providers for automatic protection of workloads
- Virtual firewall – are deployed by cloud service users internally on virtual machines to protected hosted services and applications
- Containerized firewalls provide protection to containerized applications such as Kubernetes containers
Key Components of Hybrid Cloud Security
- Physical controls secure the physical infrastructure of hybrid clouds. Access restrictions, surveillance, backup and power systems etc. are covered under physical security. Large public cloud providers having geo spanning data centers implement a plethora of security controls for underlying infrastructure / platform security.
- Technical controls are required to protect workloads, data and systems and usually include encryption, automated provisioning or deprovisioning, security orchestration, access controls and endpoint security controls.
- Administrative control includes human based policies and approaches to secure environments that usually include employee awareness and training, role specific training, and disaster recovery planning.
Best Practices of Hybrid Cloud Security
- Only trusted applications are allowed with strict policies. Block all unknown, unapproved applications to reduce the risk window. Network tools are a crucial asset here to classify traffic for complete visibility and control from application perspective.
- Identity based access controls need to be integrated into access control policies. Permissions need to be tied to the user and not to the system to have a consistent, dynamic and secure approach while the user is not stationary.
- Adopt zero trust approach – do not trust anyone, always verify is the principle which needs to be enforced be it user, device, or connection. Segmenting workloads and blocking known threats help in reducing the lateral movement of attackers in the network.
- Centralized policy management is the crux as that enforces consistent implementation across cloud and other on premises setup
- Flexible integration with security tools enhances security posture. Tools which can operate across physical, virtual or containerized workloads and scale as per business needs are ideal candidates here.
- Security operations automation helps in reducing the human errors and response is improved. The team can focus on high value security strategies.
