Table of Contents
Imagine waking up to the news that your company’s confidential information has leaked on the Dark Web or that a ransomware attack has brought critical systems down. The price of inaction? Millions of dollars, reputational harm, and operational disruption. Cyber threats are no longer an option – they are a fact. That’s why incident management solutions have become an indispensable cornerstone of cybersecurity.
Organizations everywhere are pounded by a constant tide of cyber attacks, ranging from phishing to zero-day exploits. A single forgotten vulnerability can snowball into a full-blown disaster. In response, a solid incident management process allows security teams to rapidly detect, analyze, and eliminate threats before they get out of control.
In this article, we go deep into the incident management definition, its importance in cybersecurity, the key incident management steps, best practices, and emerging technologies driving current threat response.

What is Incident Management?
Incident management is the methodical process of detecting, analyzing, and resolving security incidents to avoid interruptions in an organization’s operations. It ensures that security threats are managed effectively, minimizing downtime and protecting valuable assets.
The incident management framework offers systematic processes to detect, investigate, and contain security threats, allowing organizations to react quickly to cyber threats.
Why is Incident Management Important?
Cyber threats are constantly changing, with the attackers using new methods to compromise security . In the absence of a good incident management process, organizations face significant financial, reputational, and operational losses. Some of the most important reasons why incident management is essential are:
- Reducing downtime: Quick response to security incidents avoids extended downtime.
- Safeguarding sensitive information: Incident handling in a timely manner protects confidential data.
- Regulatory compliance: Several industries mandate that organizations possess an organized incident management process.
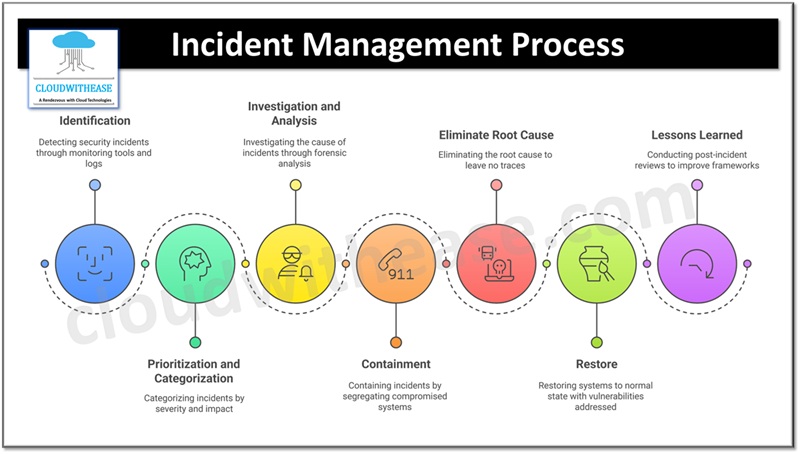
Key Steps for Incident Management Process
Incident management process adopts a structured approach to identify, analyze, and contain security threats. Some of the key incident management steps to follow are:
1. Identification: The first step is the detection of security incidents through monitoring tools, logs, and threat intelligence sources to detect anomalies in real-time.
2. Prioritization and Categorization: After they are identified, categorized incidents according to their severity and impact. This enables teams to assign resources to address high-priority threats first.
3. Investigation and Analysis: Knowledge of attack vectors allows for more effective mitigation. Security teams investigate the cause of the incident through forensic analysis and threat intelligence.
4. Containment: Containing the incident avoids greater harm which can be achieved by segregating compromised systems, banning malicious IPs, or shutting down compromised accounts.
5. Eliminate Root Cause: After containment, eliminate root cause of the incident with the help of security teams to leave no cyber attack traces.
6. Restore: Restoring impacted systems to a normal state with security vulnerabilities being addressed.
7. Lessons Learned: Post-incident reviews assist organizations in improving their incident management framework, highlighting areas of gaps and enhancing future incident response.
Incident Management Best Practices
To improve the cybersecurity posture, organizations are advised to adhere to the following incident management best practices:
- Increase the use of automation: AI enables efficient response to incidents using incident management tools.
- Train regularly: Employees ought to be educated on identifying and escalating security concerns.
- Set forth communication: Better collaboration among security personnel aids in resolving incidents faster.
- Maintain steady monitoring: To respond to incidents proactively, threats must be detected in real-time.
- Keep records: Logs are an invaluable resource for audits, investigations and future threat mitigation.
Incident Management Tools & Technologies
Organizations can take advantage of sophisticated tools for incident management that can spot, assess and mitigate security threats. These may include:
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): Aggregates and analyzes security logs to identify anomalies.
- SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response): This helps in automating response actions to mitigate threats quickly.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: This provides real-time insights into emerging cyber threats.
- Dark Web Monitoring Tools: The role of dark web monitoring tools is to help companies detect data leaks and compromised credentials.
Conclusion
Cyber threats don’t wait for companies to be ready, they hit when vulnerabilities are at peak. Incident management is not just a process; it’s a company’s defense against cyber threats. By adopting a structured incident management framework, using incident management tools, and staying ahead of attack techniques, companies can turn disasters into manageable events.
Now the real question is – will your company be caught off guard, or will you be prepared to outpace the threats of tomorrow? The answer lies in your cyber defense strategy.
